Amidst the post-earthquake fear, we managed to complete our 15 days internship in the Dermatology department which was setup in the patient’s waiting hall. The posting went pretty well; the learning experience was fun – thanks to the teachers and seniors who provided us with friendly environment and guidance. A…
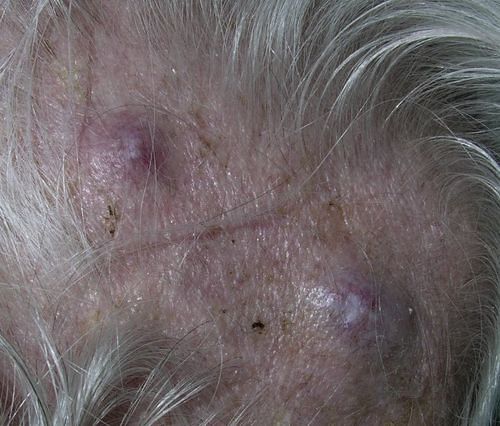
Cutaneous manifestation in thyroid disorders
Skin – Systemic Disease Connection “When a man has on the skin of his body a swelling or an eruption… and the disease appears to be deeper than the skin it is a leprous disease.” – Leviticus 13: 2-3 In ancient times changes in skin were taken to indicate the…
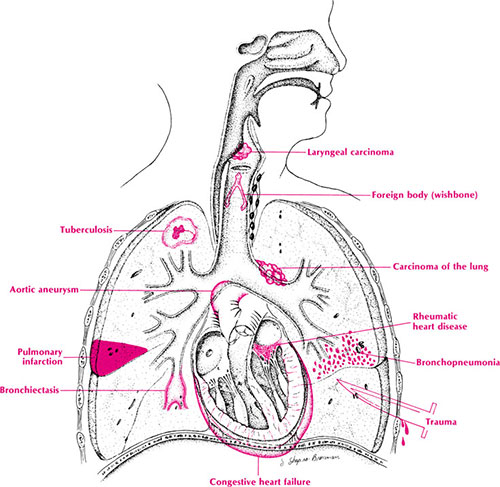
Hemoptysis – Examination and Evaluation
Synonym: Haemoptysis Definition of Hemoptysis Simple definition: Expectoration of blood or bloody sputum Hemoptysis is defined as the expectoration of blood from the respiratory tract, a spectrum that varies from blood-streaking of sputum to coughing up large amounts of pure blood. True hemoptysis is expectoration of blood from the lower respiratory tree, below…
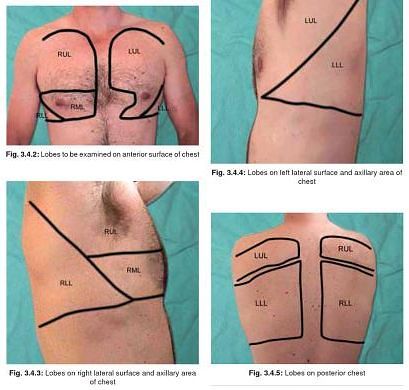
Respiratory Examination – Relevant Anatomy and Physiology
1. Division of Airway: Extrathoracic (Upper) airway: Nose to Upper trachea Intrathoracic (Lower) airway: Lower trachea to Alveoli and lungs Note: Vocal fold is also regarded as the demarcating line between upper and lower respiratory tract 2. Angle of Louis: Junction of body of sternum to manubrium (2nd costal cartilage…
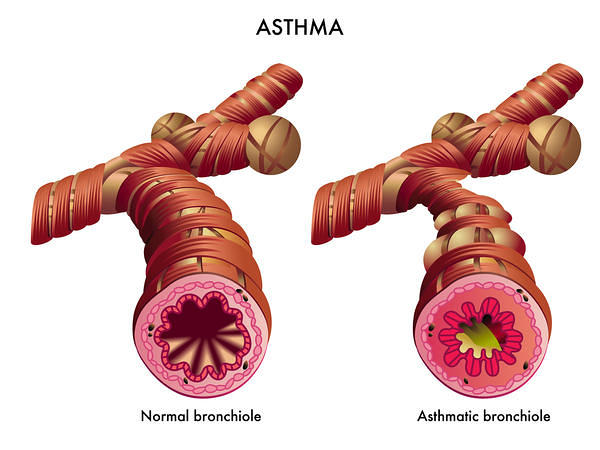
Respiratory Examination – Noisy Breathing
GRUNTING Definition: A short, explosive, moaning or crying sound heard on expiration (Child and neonates) Cause: Any cause of respiratory distress Mechanism: In attempt to increase FRC which helps to keep narrowed or collapsing airways open, creating a longer time for alveolar gas exchange STERTOR Definition: Non-musical, low pitched, snoring…
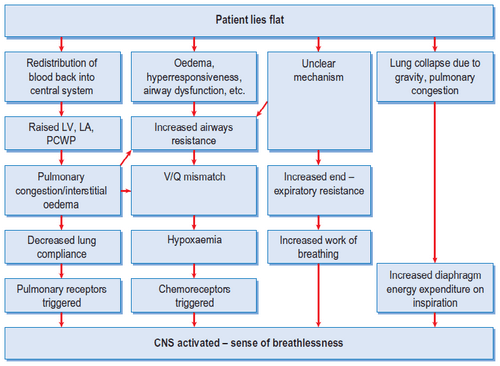
Respiratory Examination – Dyspnea
Definition: Breathlessness inappropriate to the level of physical exertion or even occurring at rest (subjective and not a sign) Mechanisms: Chemoreceptors: Peripheral: Carotid and aortic bodies (to pO2, pCO2 and H+) Central: Medulla (to pCO2, not pO2, change in pH of CSF) a. Increased work of breathing: Airflow obstruction: Bronchial…

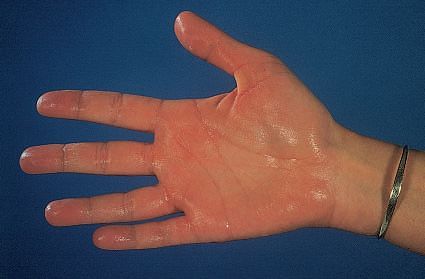
Examination of Hands
History: Hand dominance and occupation? Injury? Pain? Paresthesia? Impaired function? Swelling? Position: Place the patient’s hands on pillow Look: SEATS a. Shape or Deformity: – Wrist: Radial deviation: RA Ulnar deviation and flexion deformity: Spastic hemiplegia (CP) Wrist drop (also finger drop): Radial nerve injury Prominent dorsal ulnar and radial…

Mendelian Inheritance : Basis of Genetics
Some important terminologies Gene: a functional part of the DNA molecule of a chromosome which directs the synthesis of a specific polypeptide chain. Allele (allelomorph): alternative form of a gene found at the same locus on a pair of homologous chromosomes. Homozygous: the presence of two identical alleles at a…