The Extensor Zone VII (wrist) contains 6 extensor compartments comprising of 6 synovial sheath lined tunnels separated from each other by fibrous sheath. These compartments contain tendons of muscles that pass from forearm to hand.
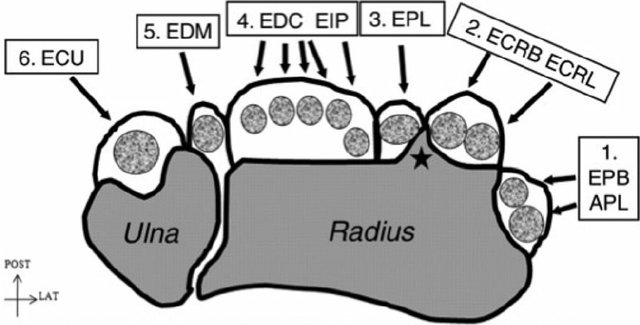
The number of tendons passinf thorugh the compartments (radial to ulnar) can be remembered using the mnemonic: 2-2-1-2-1-1.
Compartment 1: APL (Abductor Pollicis Longus; radial; frequently has multiple slips) and EPB (Extensor Pollicis Brevis; ulnar)
- Remember: These form the lateral border of Anatomical Snuff box
- DeQuervain’s tenosynovitis (modified Eichoff’s test or Finkelstein’s test) – most common extensor compartment tenosynovitis
Compartment 2: ECRL (Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus) and ECRB (Extensor Carpi Radilis Brevis)
- Intersection syndrome: the intersection (at an angle of around 60°) of the musculotendinous junctions of the first and second extensor compartment tendons leading to tenosynovitis of 2nd compartment due to friction from the overlying 1st compartment.
Lister’s tubercle separates Compartment 2 from Compartment 3.
Compartment 3: EPL (Extensor Pollicis Longus)
- Remember: This forms the medial border of Anatomical Snuff box
- Drummer’s wrist: Drummers, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Distal radius fractures
Compartment 4: EDC (Extensor Digitorum Profundus; radial) and EIP (Extensor Indicis Proprius; ulnar) + Posterior interosseous nerve (PIN)
- Tenosynovitis (more diffuse) may be confused with Ganglion cyst (more compact)
Compartment 5: EDM (Extensor Digiti Minimi)
- 1st tendon to rupture in Vaughan-Jackson syndrome (commonly seen in Rheumatoid Arthritis – sequential atraumatic rupture of extensor tendons in hand starting from ulnar side and progressing radially)
Compartment 6: ECU (Extensor Carpi Ulnaris)
- Snapping ECU: ECU tendon subluxates producing painful “snap” during extension and supination and reduces with pronation.
ECU subsheath is a part of TFCC.
The PIN (Posterior interosseous nerve from Radial nerve) innervates the EDC, EDM, and ECU muscles from the superficial wrist extensor compartment. It then innervates the APL, EPB, EPL, and EIP muscles.

Interesting and simplified with clinicals immediately followed
Excellent description. Wonderful explanation of all the detail’s.
There is a typo in this “The number of tendons passinf thorugh the compartments (radial to ulnar) can be remembered using the mnemonic: 2-2-1-2-1-1.” following the picture! Great work just wanted to let you know!