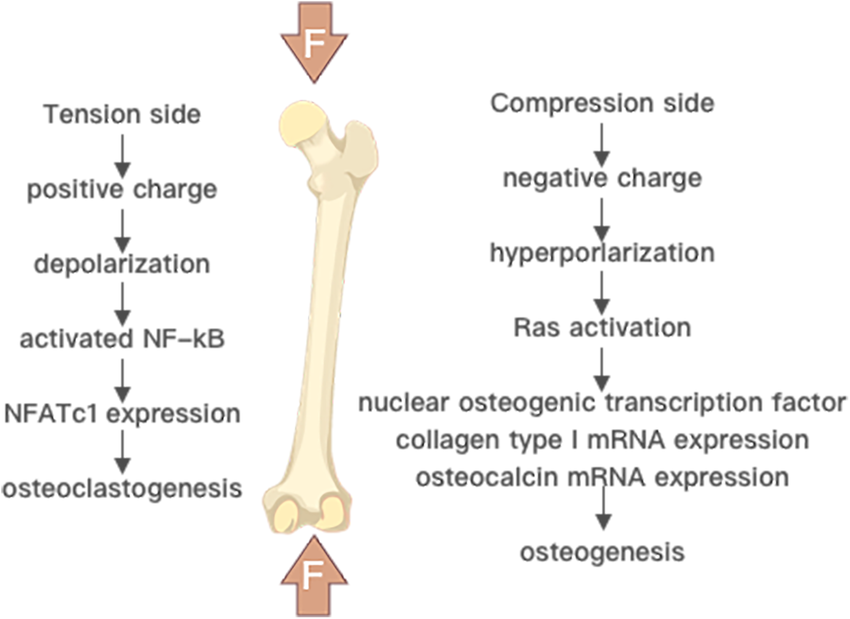
Bone remodeling involves the removal of mineralized bone by osteoclasts followed by the formation of bone matrix through the osteoblasts that subsequently become mineralized.
There are 2 prominent concepts of bone remodelling:
1. Hueter-Volkmann law or Delpech’s law: It states that bone growth in the skeletally immature is inhibited in regions exposed to high stress and stimulated in regions of low stress.
Example: Progression of coronal plane deformity in idiopathic scoliosis – higher stress in concave side and lower stress in convex side
2. Wolff’s law: In skeletally mature, bone is laid down in areas of high stress and reabsorbed in areas of low stress.
Piezoelectricity, also referred to as the piezoelectric effect, is the ability of certain solid materials to generate an electric field in response to mechanical deformation. The piezoelectricity induced by mechanical deformation of bone is a negative electrical charge in areas of bone compression and a positive charge in the areas of traction.
Examples:
- Bone spurs or osteophytes: Synthesis of more bones due to increased stress of underlying bone in region of deteriorated and dehydrated intervertebral disc
- Bone loss after chronic unloading: Reduced bone mineral density in cases of unloading due to paralysis