Relevant terms and definitions:
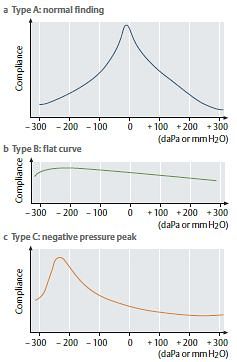
1. Tympanogram: plots compliance changes of the Tympanic Membrane (TM) versus air pressure in the EAC
- Y-axis shows pressure gradient and X-axis shows compliance change
2. Peak: point on the tympanogram that represents the point of maximum compliance, in which pressure of the external ear canal equals the pressure of the middle ear space (function of eustachian tube)
3. Compliance: sound absorption
4. Impedance: resistance
Principle:
- Oscillator emits sound (usually 220 Hz) into the ear canal. The sound is absorbed by the tympanic membrane and the non-absorbed sound is reflected back which is picked up by Microphone.
- Air pump generates positive or negative pressure in the ear canal.
- Maximum compliance of TM denotes equal pressure in EAC and middle ear.
- The greater the positive or negative pressure in the ear canal, greater the “acoustic stiffness” of the tympanic membrane and lower is the compliance. Less compliant TM absorbs less sound and reflects more sound.
Note: It is not performed in infants < 7 months due to suppleness of cartilage of external canal which may produce misleading result.
Types and Interpretation:
1. A: normal peak between –100 and +100 daPa
2. A’s’: “shallow” peak (reduced compliance), TM stiff; suggests otosclerosis or tympanosclerosis
3. A’d’: “deep” peak (hypercompliant), TM flaccid; suggests ossicular discontinuity or a “monomeric” TM
4. B: flat, no peak, nonmobile TM; suggests effusion, perforation, or an open PE (pressure equalization) tube
- Normal EAC volume: Otitis media with effusion (OME)
- Decreased EAC volume: Wax
- Increased EAC volume: Perforated TM
4. C: peak shifted to a more negative pressure (<–100), retracted TM; suggests eustachian tube dysfunction or TM atelectasis
5. EAC volume: normal for children is 0.5-2 mL, adults is 1-3 mL