You must be asking yourself – “how to remember the TNM staging system?” and looking here and there for mnemonics only to find nowhere. Understanding the oncoanatomy helps to understand the staging system of the cancers.
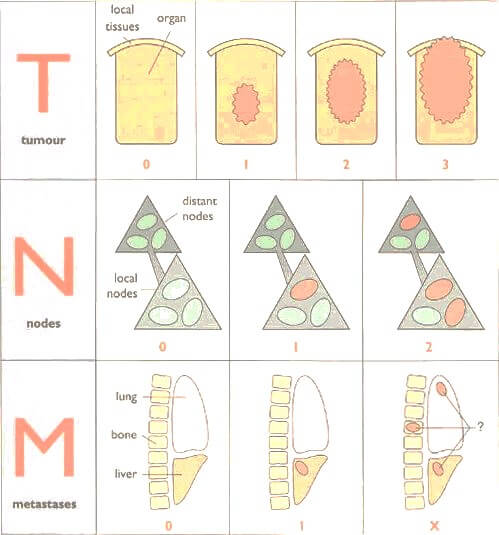
Tumor Status (T)
| T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | |
| Depth of invasion | ||||
| Solid organs | Confined | Capsule, muscle | Bone, cartilage | Viscera |
| Hollow organs | Submucosa | Muscularis | Serosa, adjacent/surrounding structures | Viscera |
| Mobility | Mobile | Partially Mobile | Fixed | Fixed and destructive |
| Neighboring structure | Not invaded | Adjacent (attached) | Surrounding (detached) | Viscera |
| Surface spread | ||||
| Regions (R) | ½ of R1 | R1 | R1 + R2 | R1 + R2 + R3 |
| Circumference | ≤ 1/3 | > 1/3 – 1/2 | > ½ – 2/3 | > 2/3 |
| Size | ||||
| Diameter (cm) | ≤ 2 | 2 to 4-5 | > 4-5 | > 10 |
Size of T1 in various tumors
Head and neck, Parotid, Thyroid, Breast, Liver, Pancreas, Anus, Skin: ≤ 2 cm
- 2-5 cm is T2 in breast carcinoma and >5 cm is T3 and extension to chest wall is T4.
- 2-4 cm is T2 in head and neck cancers including thyroid and >4 cm is T3 and invasion of adjacent structures is T4.
- >5 cm (atleast 1 of the multiple nodes) is T3 in liver as well but T2 is <5 cm with multiple nodes or requires vascular invasion.
- T4 is invasion of adjacent structures other than gallbladder or with visceral peritoneum.
Lungs: ≤ 3 cm
- 3-7 cm is T2 in lung cancer and >7 cm is T3.
Cervix: < 4 cm
- >4 cm is T1b2.
Soft tissue sarcomas: ≤ 5 cm
- >5 cm is T2.
- There are no T3 and T4.
Kidney: ≤ 7 cm
- >7 cm is T2.
- Local invasion within Gerota’s fascia (including adrenal glands and IVC) is T3.
- Invasion beyond Gerota’s fascia is T4.
Bone: < 8 cm
- >8 cm is T2
- Skip lesions at primary site is T3
- There is no T4
Nodal Status (N)
| N1 | N2 | N3a | N3b,c | |
| Station | First (regional) | First | First | Second (juxtaregional) |
| Drainage | ||||
| Unilateral | Ipsilateral | Ipsilateral | Ipsilateral | Contralateral |
| Bilateral | Ipsilateral | Contralateral or bilateral | Ipsilateral or contralateral | Distant |
| Number | Solitary | Multiple 2-3 | Multiple 4-9 | Multiple 10-16 |
| Size (cm) | <2-3 | >3 | >5 | >10 |
| Mobility | Mobile | Partial attached muscle invasion | Fixed to vessels, bone, skin | Fixed and destructive |
Lymph node sizes
Head and neck tumors:
3 Nodal stages 3 cm increment in sizes
- N1: ≤3 cm
- N2: 3-6 cm
- N3: >6 cm
Genitourinary tumors (only Testes and Renal pelvis):
- N1: ≤2 cm
- N2: 2-5 cm
- N3: >5 cm
Lymph node numbers
Head and neck cancers, Urinary Bladder Cancer:
- N1: Solitary node
- N2: Multiple nodes
Colorectal carcinoma:
- N1: 1-3
- N2: ≥4
Gastric carcinoma:
- N1: 1-2
- N2: 3-6
- N3: >6 (a – 7 to 15; b – >15)
General Idea for Staging According to TNM classification
| T1 | T2 | T3 | T4a | T4b | |
| N0 | Stage I | Stage II | |||
| N1 | Stage III | ||||
| N2 | Stage IVA | ||||
| N3 | Stage IVB | ||||
| M1 | Stage IVC | ||||
Correlation between the Tumor stage (T) and ease of nodal (N) involvement based on whether the regional lymph node basin is within or outside the capsule or serosa gives an idea about staging the malignancy.
When regional lymph nodes are within the capsule or serosa: T1 or T2 = N1
- Lung: N1 (hilum and other intrapulmonary nodes) are within pleura
- Breast: N1 (Level I and II axillary) and N2 (internal mammary nodes) are adjacent to breast tissue (also extensive subcutaneous lymphatics)
- Stomach: Lymph nodes in Muscularis propria (Beyond serosa in other GI tracts)
- Penis and urethra: Rich subcutaneous lymphatics drain to juxtaposed femoral nodes at the crura of penis without a capsule.
When regional lymph nodes are beyond the capsule: T3=N1
- Pancreas
- Gallbladder
- Kidney
- Ovary
- Fallopian tube
- Uterine fundus
- Cervix
- Vagina and Vulva
When regional lymph nodes are beyond the serosa in hollow organs: T4=N1
- Colon
- Rectum
- Urinary bladder
- Renal pelvis
- Testis
Esophagus has a thin adventitia, and therefore, T3=N1.
When regional lymph nodes are distant to primary sites: T4=N1
- Skin cancer
- Melanoma
- Merkel cell cancer
- Soft tissue and bone sarcomas
Separate Stage
Testicular cancers
- M1a = Non-regional nodes metastases = stage III
- M1b = Lungs metastases = stage IV
Trophoblastic tumors
- M1a = Lung metastases = stage III
- All other distant metastases = stage IV
Hematologic malignancies
Most hematologic malignancies have separate staging system, example – Ann Arbor Staging for Hodgkin’s Lymphoma.
Source: TNM Staging Atlas with Oncoanatomy 2nd edition By Philip Rubin, John T. Hansen
a very good summery but i have a few notes,1st of all the first line regarding the T of solid organ,T2 that u mentioned to be capsule and muscle invasion dosnt apply to many …like kidney,breast ,or even liver…explain it to me please…many thanks for ur effort
That is just a general idea and may not be applicable to many.
2ndly what is meant by R1 R2 R3?
RO Resection: complete resection with no microscopic residual tumor (margins are microscopically negative according to the pathologist).
R1 Resection: complete resection with no grossly visible tumor as defined by the surgeon, but microscopic cancer may be left behind (margins are microscopically positive according to the pathologist).
R2 Resection: partial resection, with grossly visible tumor left behind.
Loved your website, very informative and useful, keep the good work going.
Thanks alot !