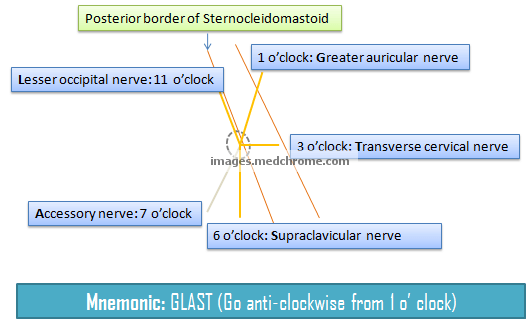
This is a visual mnemonic for the nerve arrangement of superficial cervical cutaneous branches of cervical plexus. This mnemonic was created only for the ease to remember and may not resemble exact anatomy.
The site of injection for superior cervical plexus nerve block is the midpoint of posterior border of sternocleidomastoid. Assuming this as a center point, the various position of nerves, from north going anti-clockwise is given by mnemonic “GLAST”:
- 1 o’ clock: Greater auricular nerve (C2,C3) – Innervates skin over the parotid gland, angle of jaw and posterior ear
- 11 o’ clock: Lesser occipital nerve (C2) – Innervates scalp behind and above ear
- 7 o’ clock: Spinal accessory nerve (XI) – This doesn’t belong to superficial cervical plexus and lies deep to the sternocleidomastoid muscle and innervates sternocleidomastoid and trapezius
- 6 o’ clock: Supraclavicular nerve (C3,C4) – Divides into medial, intermediate and lateral branches and supply sensation over shoulder, lateral neck and anterior upper thoracic wall
- 3 o’ clock: Transverse cervical nerve (C2, C3) – Innervates skin of front and side of neck (anterior triangle)
All these nerves are also the contents of the occipital triangle of neck. Except spinal accessory nerve, all these nerves crosses superficial to the sternoclediomastoid muscle. In general, the superficial cervical plexus supply the skin of anterolateral neck. Superficial cervical plexus block is indicated for skin surgeries of head and neck.
Origin of cervical plexus: anterior rami of the C1 – C4 nerve roots
Location of cervical plexus: anterior to the cervical vertebrae and posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle.
Components of cervical plexus:
- Cutaneous branches, which supply the lesser occipital, greater auricular, transverse cervical, and supraclavicular nerves
- Ansa cervicalis, which innervates the infrahyoid and geniohyoid muscles
- Phrenic nerve, which is the only motor nerve to innervate the diaphragm
- Contributions to the accessory nerve (CN XI), which innervates the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles
- Direct muscular branches, which supply prevertebral muscles of the neck.
Procedure:
Insert the needle ( 22-gauge, 5-cm, short bevel needle) at the midpoint of the posterior border of the sternocleido – mastoid muscle to approximately half the depth of the muscle, and inject 3 to 4 mL of local anesthetic. Also perform a subcutaneous injection of additional local anesthetic cephalad and caudad along the length of the sternocleidomastoid muscle posterior border.