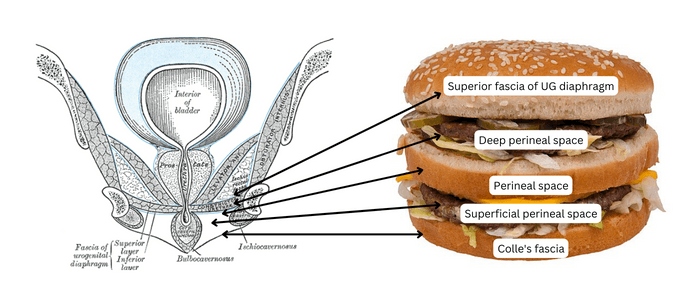
Superficial and deep perineal space is located in the urogenital triangle, the boundaries of which are:
- Apex: Pubic symphysis
- Two sides: Ischiopubic ramus
- Base: A line connecting 2 ischial tuberosity
Analogy: Remember a big mac. It has 3 layers of BUN and 2 hamburger PATTIES.
- BUN = Fascia
- Bottom bun = Superifical perineal fascia (Colle’s fascia – continuous with Scarpa’s fascia)
- Middle bun = Inferior fascia of urogenital diaphragm (perineal membrane – anchoring point for erectile tissues)
- Top bun = Superior fascia of urogenital diaphragm
- PATTIES = Space
- Between Bottom bun and Middle bun (bottom PATTY) = Superficial perineal space
- Between Middle bun and Top bun (top PATTY) = Deep perineal space
Posteriorly, all 3 Fascias are attached to the perineal body, closing the spaces.
Superficial Perineal Space
Mnemonics:
1. Superficial to Perineal membrane
2. Sexually Pleasurable Structures
3. 4 arteries/nerves, 3 muscles, 2 erectile tissues, 1 gland/duct
Contents:
- 3 muscles:
- Ischiocavernosus
- Bulbospongiosus
- Superficial transverse perineal muscles (2)
- 2 erectile tissues:
- Crus of penis or clitoris (deep to ischiocavernosus)
- Bulb of penis or vestibule (just under bulbospongiosus)
- 1 gland/duct:
- Greater vestibular glands (Bartholin’s glands) in females
- Duct of bulbourethral glands in males
- Arteries and nerves: “Perineal and Posterior”
- Perineal artery (internal pudendal artery branch)
- Posterior scrotal/labial artery (from perineal branch)
- Posterior scrotal/labial nerve (from perineal branch of pudendal nerve)
- Perineal branch of posterior cutaneous nerve of thigh
Deep Perineal Space
2 muscles:
- Deep transverse perineal muscles
- External urethral sphincter
1 gland:
- Bulbourethral glands in males
Arteries and nerves: “Deep and Dorsal“
- Deep and Dorsal artery of penis/clitoris
- Artery of bulb of penis/vestibule
- Urethral artery (internal pudendal artery branch)
- Dorsal nerve of penis/clitoris (branch of pudendal nerve)