Synonyms:
Strawberry gallbladder is also known as hyperplastic cholecystoses. Hyperplastic cholecystoses are a spectrum of non-neoplastic proliferative disorders caused by deposition of cholesterol-laden macrophages within the wall of the gall bladder. The cholecystose range from abnormalities of the gallbladder wall (adenomyomatosis and strawberry gall bladder) to gallbladder polyps extending into the lumen.
Definition:
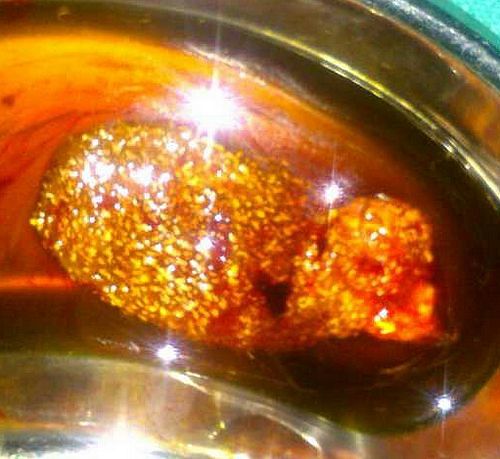
Cholesterolosis occurs due to the accumulation of cholesterol esters and triglycerides in subepithelial macrophages and gallbladder epithelium. It is associated with bile supersaturation with cholesterol, but not with increased serum cholesterol. It is usually asymptomatic and detected incidentally in 30-50 % of cholecystectomy specimens. Cholesterolosis occurs in 2 major forms: localized and diffuse. Strawberry gallbladder refers to diffuse cholesterolosis characterized by tiny mural cholesterol deposits likened to strawberry seeds. It is a pathologic diagnosis rather than a clinical diagnosis.
Clinical features:
This is usually asymptomatic but sometimes may exhibit mild symptoms such as indigestion, gas and distress after meals. Pain in the upper quadrant is also noted.
Epidemiology:
In a Survey done to determine the association between cholesterolosis and gall bladder malignancy following results were observed :
- Sample: 3123 cases
- Gender predominance: more common in women than in men
- Cholesterolosis has a strong negative association with gallbladder cancer
Gross features:
- Yellow, flat deposits on mucosal surface, focal or diffuse.
- May have speckled appearance (“strawberry gallbladder”), 20% are associated with cholesterol polyps.
- Polyps vary in size from 1-10 mm.
- Bile in the lumen is generally dark and thick, with a high concentration of cholesterol and sometimes floating yellow lipid particles (lipoidic corpuscles).
Microscopic features:
- Foamy macrophages in lamina propria and epithelium.
- Villous mucosal hyperplasia with macrophages at tips of villi.
- Usually no or minimal cholecystitis.
- Usually changes are restricted to gallbladder and don’t involve extrahepatic bile ducts.
Ultrasound features:
- Brightly echogenic non-mobile masses, with a ring down/ comet tail or reverberation artefact.
- No posterior acoustic shadowing.
- When cholesterosis is focal, it forms cholesterol polyps.
Primary concern:
Rule out gall bladder malignancy.
Submitted by: Dr. Sulabh Shrestha