Indications for surgery
| Age group | Spondylolisthesis | Indications |
| Pediatric | Low grade | Failure to respond to conservative treatment (9-12 months) Progressive slippage Intractable low back or radicular pain Neurological deficit and deterioration |
| High grade | Neurological symptoms Severe sagittal plane spinal deformity | |
| Adult | Low grade | Failure of non-operative treatment Progressive slippage Symptomatic and radiographically unstable isthmic spondylolisthesis |
| High grade | Disabling back and/or low back pain |
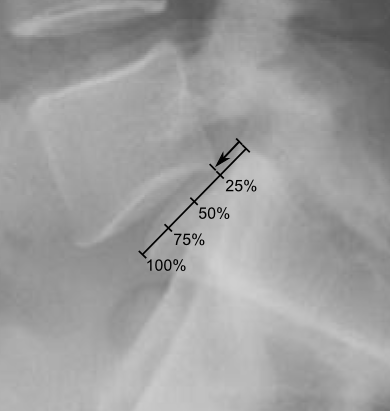
SDSG classification
Mnemonic: SDSG
1. SDSG classification
2. Degree of slip
3. Spinopelvic balance
4. Global spinal balance
| Degree of slip | Spinopelvic balance | Global spinal balance | Type | Remarks | Surgery |
| Low grade (Meyerding I and II) | PI <45 (low PI) | C7 plumb line falls over or behind femoral head (Balanced) | 1 | Nutcracker – clamping of posterior element of L5 between pars interarticularis of L4 and S1 during extension | Instrumentation and fusion Postural reduction |
| PI 45-65 (normal PI) | 2 | ||||
| PI >65 (high PI) | 3 | Shear type – | |||
| High grade (Meyerding III, IV, V) | SS > PT (Balanced) | 4 | |||
| PT > SS (Unbalanced), i.e., retroverted pelvis | 5 | Reduction and realignment should be considered | |||
| PT > SS (Unbalanced), i.e., retroverted pelvis | C7 plumb line falls anterior to femoral head (Unbalanced), i.e., stooping | 6 | Reduction and realignment are mandatory |
Degenerative spondylolisthesis Instability Classification
| Parameter | Type I, Stable | Type II, Potentially unstable | Type III, Unstable |
| LBP | None or very mild | Primary or secondary symptom | Primary or secondary symptom |
| Restabilization sign | Present Grossly narrowed disc height | Some Reduced disc height | None Normal to slightly reduced disc height |
| Disc angle | Lordotic disc angles on flexion radiographs or <3 mm translation on dynamic films | Neutral disc angle on flexion radiographs or 3-5 mm of translation on dynamic films | Kyphotic disc angle on flexion radiographs or >5 mm translation on dynamic films |
| Joint effusion | No facet joint effusion on MRI | Facet joint effusion on MRI without distraction | Large facet joint effusion on MRI |
| Surgery | Decompression alone | Decompression and posterior fusion | Decompression and posterior fusion and interbody fusion |
General alignment targets
- PI – LL < 10°
- PT < 25°
- SVA < 5 cm