The essence of this approach is that, rather than requiring a highly specialized nutritionist, a systematic assessment on the part of all the disciplines that are interacting with the patients can achieve what is needed for the nutritional care of the older patient with a fragility fracture, regardless of setting or healthcare provider.
S – Screen for nutritional risk
- 2 step process
- First pass screening (can be done by anybody with minimal training) – skipped in high risk settings like acute hip fractures due to low sensitivity
- Mini Nutrition Assessment – Short Form
- Malnutrition Screening Tool
- Malnutrition Universal Screening Tool
- Detailed assessment (done by a qualified health professional) – for patients screened as “at risk” by Step 1
- First pass screening (can be done by anybody with minimal training) – skipped in high risk settings like acute hip fractures due to low sensitivity
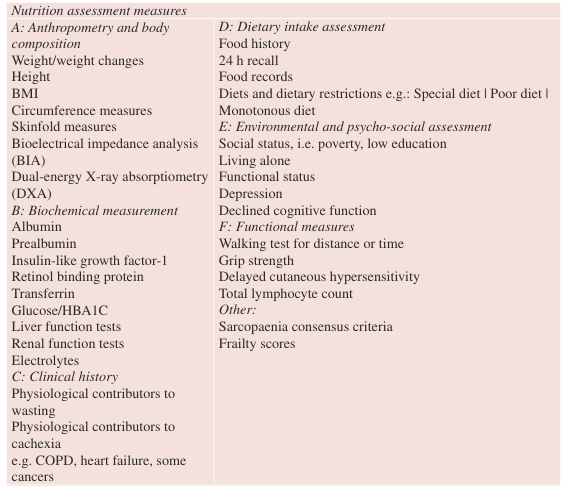
I – Interdisciplinary assessment (ABCDEF mnemonic)
- Anthropometry and body composition
- Biochemical markers
- Clinical assessments and measures
- Diet and medication history
- Environmental and psycho-social factors
- Functional measures
M – Make the diagnosis (es)
- Subjective Global Assessment
- Mini Nutritional Assessment – Short Form
- Global Leadership on Malnutrition Criteria
- ESPEN Criteria
- ICD-10AM Criteria
P – Plan with the patient
A comprehensive nutrition care plan should consider:
- Short- and long-term nutritional goals with the patient
- Nutrient and fluid requirements
- Patient education and instructions for how to implement the nutrition intervention
- Estimated duration of the nutrition therapy
- Clinician re-assessment and monitoring parameters
- Discharge planning, continuity of care
- Contacts and further information sources

L – impLement interventions
- Improving access for nourishing foods and fluids, both in health care settings and for those living at home
- Oral nutrition supplements
- Nutritional support (enteral/parenteral nutrition)
- Prescription and Deprescription of medications and therapies
- Nutrition education, counselling and psychosocial support
- Coordination of nutrition care interventions
Nutrition care plan is included in handover and discharge documentation, and is transferred to the next setting and health care provider/s.
E – Evaluate ongoing care requirements
- Patients with or at risk of a nutrition-related diagnosis will routinely require nutrition monitoring or re-assessment strategies. Processes for re-screening should also be considered for those not currently at risk.
Further reading: