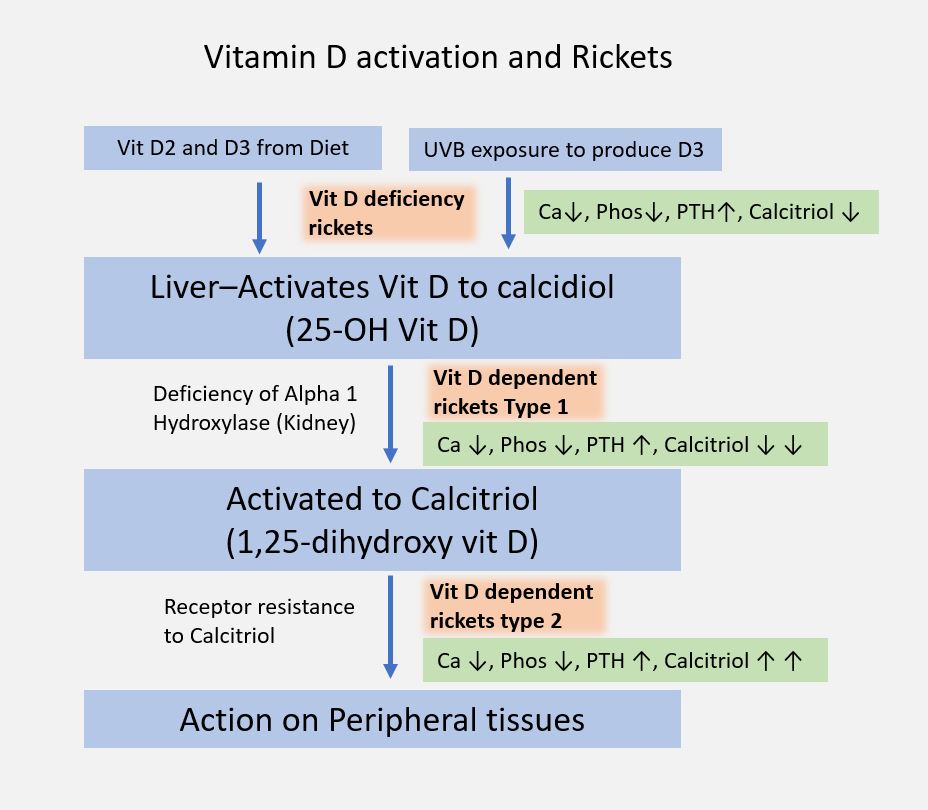
Types
| Type | Pathology | 25(OH) D | 1,25(OH)2 D | PTH | Ca | PO4 | ALP | Additional clinical findings | Treatment |
| Vitamin D deficiency (Nutritional) | Hypovitaminosis D 🡢 Hypocalcemia 🡢 Secondary hyperparathyroidism 🡢 Rise of serum calcium towards normal level | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ | ↓/= | ↓ | ↑ | Rachitic rosary Bowing of knees Muscle hypotonia Waddling gait Dental disease Looser zones/Milkman’s fracture (pseudofracture on compression side) | Stoss regimen: Vitamin D 3-6 lac IU PO/IM as 2-4 doses in 1 day OR Oral Vitamin D 2000-5000 IU/day over 4-6 wks |
| Calcium deficiency (Nutritional) | Hypocalcemia 🡢 Secondary hyperparathyroidism 🡢 Enhanced renal conversion of 25(OH)D to 1,25(OH)2 D and Rise of serum calcium towards normal level | = | ↑/= | ↑ | ↓/= | ↓ | ↑ | Same as above | Oral calcium 700 mg/day |
| Phosphate deficiency (Nutritional) | Hypophosphatemia 🡢 Increased renal production of 1,25(OH)2 D | = | ↑↑↑ | = | = | ↓ | ↑ | No features of secondary hyperparathyroidism | Oral supplementation of phosphate |
| Vitamin D dependent rickets/VDDR type I (pseudo-vitamin D deficiency) | AR inheritance Defect in renal 1α-hydroxylase | ↑/= | ↓↓↓ | ↑ | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ | Oral physiologic doses of Calcitriol/1,25(OH)2 D: 1-2 mcg/day | |
| Vitamin D dependent rickets/VDDR type II | AR inheritance Receptor defect for 1,25(OH)2 D | ↑/= | ↑↑↑ | ↑ | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ | Alopecia | Pharmacological doses of Calcitriol or Alphacalcidiol (3-6 mcg/day) for 3-6 months + Oral elemental calcium 3 gm/day |
| Hypophosphatemic rickets (Vitamin D resistant rickets) | X-linked dominant inheritance Defefct in tubular (PCT) reabsorption of phosphate leading to phosphate “spilling” in urine (phosphate diabetes) | = | = | = | = | ↓↓↓ | ↑ | Classic triad: 1. Hypophosphatemia 2. Lower limb deformities 3. Stunted growth rate | Oral elemental phosphate 1-3 gm/day + High dose vitamin D 20,000-70000 IU/day (to counteract hypocalcemic effect of phosphate administration) |
| Hypophosphatasia | AR inheritance Error in tissue-nonspecific isoenzyme of ALP (TNSALP) 🡢 Disrupts bone mineralization | = | = | = | ↑ | ↑ | ↓↓↓ | Early teeth loss | Infusion of plasma rich in ALP activity Bone marrow transplantation |
Clinical features
Mnemonic: RICKETS
- Rachitic rosary
- Increased lordosis
- Craniotabes (<6 months)
- Knock knees (>1 year)
- Epiphysis enlargement (>6 months)
- Teeth eruption delay, Tone decreased, Tetany (<6 months)
- Skull bossing, Sternal prominence/pectus carinatum(>6 months), Seizures (<6 months)
Rickets evaluation
Mnemonic: ABCDEF
ALP: If decreased – consider Hypophosphatasia (elevated urinary phosphoethanolamine is diagnostic)
Bicarbonate: Low in Renal tubular acidosis (RTA)
Calcium: Increased/normal in hypophosphatemic rickets (Vitamin D resistant rickets/Albright syndrome) and hypophosphatasia (AR)
D Vitamin level: Increased in Vitamin D dependent rickets (VDDR) or calcium/phosphate deficiency and Normal in hypophosphatemic rickets and hypophosphatasia
- In VDDR type I, only 1 metabolite is elevated (Calcidiol)
- In VDDR type II, both the 2 metabolites are elevated (Calcidiol and Calcitriol)
Elevated PTH: Except in hypophosphatemic rickets and hypophosphatasia
FGF23: High in hereditary (XLD) and acquired forms of hypophosphatemic rickets
Fosforous (Phosphorous): High in hypophosphatasia and renal failure
Radiological features
Mnemonic: RICKETS
- Rarefaction (osteopenia)
- Indistinct cortex
- Coarse trabeculation, Coxa vara, Codfish vertebra
- Knee, wrists and ankles affected predominantly
- Epiphyseal plates widened (earliest and specific), irregular and delayed appearance of ossification centers
- Tremendous metaphysis (cupping, fraying, splaying), Triradiate pelvis (protrusion of hip and spine into soft pelvis)
- Spur (metaphyseal)
Your mnemonics blows my mind. Thank you 🙏