Relevant terms and definitions:
1. Pure tone: A single frequency sound
2. Audiometer: Equipment used to generate pure tones of varying frequency and loudness and control their presentation
3. Air conduction (AC) threshold: lowest level dB HL (hearing threshold) at which the subject perceives 50% of pure tones introduced via earphones or speakers
- Represents conduction from the auricle to the cochlea
- Measured between 125 to 8000 Hz (frequencies < 125 Hz are difficult to distinguish from vibratory sensations and with > 8000 Hz sound pressures cannot be accurately calibrated for ordinary headphones)
4. Bone conduction (BC) threshold: lowest level dB HL (hearing threshold) at which the subject perceives 50% of pure tones introduced via a bone oscillator apparatus
- Represents conduction from the bones of the skull to the inner ear (bypassing the TM and ossicles)
- Measured between 250 to 4000 Hz
5. Pure-Tone Average (PTA): average thresholds for the speech frequencies (500, 1000, 2000 Hz)
- Typically should be within 10 dB of the speech reception threshold
6. Air–Bone Gap (ABG): dB difference between bone and air conduction thresholds
- AC thresholds can only be equal to or greater than BC thresholds
- A Bone vibrator requires considerably more energy to produce sound than headphones, which is why the threshold for bone conduction can be measured only to maximum values that are 40-50 dB lower than those for air conduction
7. Masking: It means presenting a constant noise to the nontest ear. It is done to prevent non-test ear from detecting the sound presented to the test ear by crossover. It is usually done when:
- ABG > 10db.
- The difference between the AC thresholds of the right and left ear > 40db.
Adult Hearing Loss Level (WHO):
- <25 dB: normal (no difficulty with faint speech)
- 26–40 dB: mild (difficulty with faint speech)
- 41–55 dB: moderate (difficulty with normal speech)
- 56–70 dB: moderately severe (difficulty even with loud speech)
- 71–90 dB: severe (can understand only shouted speech)
- 91+ dB: profound (cannot understand even shouted speech)
Symbols:
- AC unmasked : Left ear (X) and Right ear (0)
- AC masked: Left ear ([]) and Right ear (Δ)
- BC unmasked: Left ear (>) and Right ear (<)
- BC masked: Left ear (]) and Right ear ([)
Interpretation:
1. Normal: AC threshold not > 25 dB and BC threshold not > 25 dB
2. Conductive Hearing Loss (CHL): AC threshold > 25 dB, BC threshold < 25 dB, A-B gap > 10 dB
- BC threshold normal; presence of ABG
- Maximal CHL is 60 dB (ossicular chain discontinuity with an intact TM)
3. Sensory-Neural Hearing Loss (SNHL): AC threshold > 25 dB, BC threshold > 25 dB, A-B gap < 10 dB
- AC and BC threshold below normal and similar
- No ABG
4. Mixed Hearing Loss: AC threshold > 25 dB, BC threshold > 25 dB, A-B gap > 10 dB
Special patterns:
1. Low-Frequency SNHL: Endolymphatic hydrops (Meniere’s disease)
2. Bilateral High-Frequency (Down-sloping) SNHL: Presbycusis, ototoxicity, acoustic neuroma
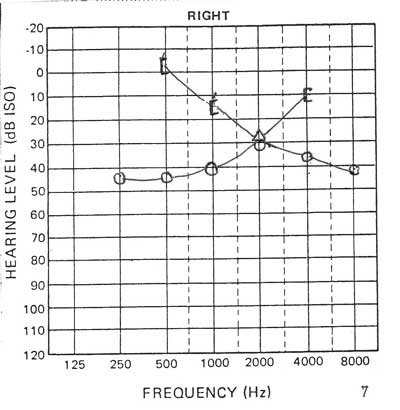
3. Carhart Notch: falsely depressed bone conduction at 2000 Hz in otosclerosis, secondary to a reduction of the inertial component of bone conduction (stapes fixation)
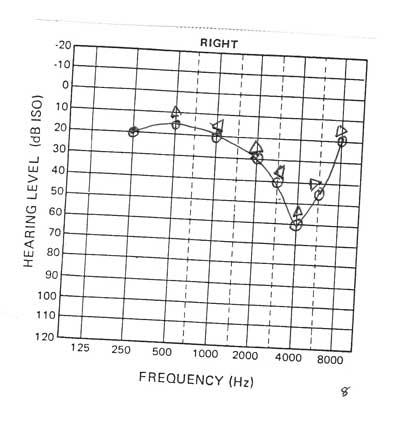
4. 4 KHz Notch (Acoustic dipping): high-frequency SNHL at 4000–6000 Hz from noise induced hearing loss (dipping of both AC and BC)
5. Cookie Bite (U-Shape): some forms of hereditary hearing loss

excellent treatise,simple and lucid.