Indications for surgery:
1. Reduced vision secondary to:
- Threatens visual axis: Pterygium advancing toward or already impinging visual axis
- Induced astigmatism: Due to flattening of meridian of pterygium by fibrosis in atrophic stage
2. Cosmesis
3. Significant discomfort not relieved by medical therapy
4. Diplopia: Resulting from limited ocular motility secondary to muscle restriction
Surgical modalities:
1. Simple excision
2. Simple excision with bare sclera technique (90% recurrence)
3. Excision with adjunctive measures:
- Postoperative Beta-radiation
- Thiopeta drops
- Intraoperative and Postoperative mitomycin C
- Conjunctival autografting (5% recurrence)
- Amniotic membrane autografting
- Keratectomy and Lamellar keratoplasty: For recurrent recalcitrant pterygium
Procedure:
1. Anesthesia: Topical anesthesia
2. Preparation and draping: Cleanse eyelashes and lid margins with Povidone-iodine 5% on a cotton-tipped applicator and place 1-2 drops of povidone-iodine in fornix
3. Insert universal eye speculum
4. Forced duction test: To rule out any restriction of rectus muscle
5. Position eye with stay sutures and clamp
6. Demarcate the body of pterygium with cautery
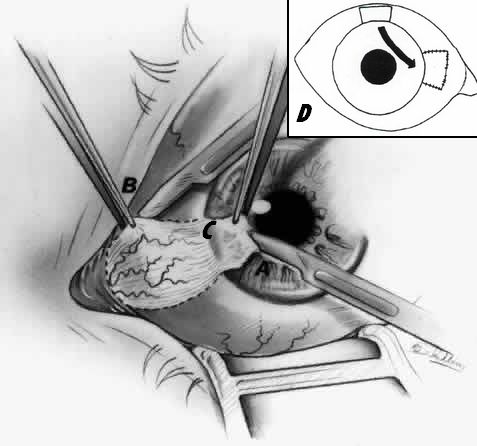
B: Removal of tail of pterygium
C: Removal of neck of pterygium
D: Bare sclera covered by conjunctival autograft
7. Remove head of pterygium (corneal portion): Lift and dissect off the cornea
8. Remove tail of pterygium (episcleral portion): Use Westcott scissors to cut along previously placed cautery marks; undermine pterygium with scissors and remove all pterygium and underlying tissue (including tenon’s capsule) down to bare sclera
9. Remove neck of pterygium (limbal portion): Using sharp and blunt dissection with scissors
10. Achieve hemostasis with the help of cautery
11. Polish the limbus with diamond burr to smoothen it
12. Next step differs depending upon the technique:
- Simple excision: Conjunctiva is sutured back to cover the sclera
- Bare sclera technique: Some part of conjunctiva is excised and its edges are sutured to the underlying episcleral tissue leaving some bare part of sclera
- Conjunctival membrane autograft: Free conjunctiva from the same or opposite eye may be used as a graft to cover the bare sclera
- Adjunct therapy with mitomycin C: Place Mitomycin C (MMC) soaked sponge onto the bare sclera for 2 minutes
- Amniotic membrane graft: Amniotic membrane graft 1mm oversized on all sides is used to cover the bare sclera
13. Apply topical combination antibiotic and steroid ointment
14. Place light pressure patch and fox shield