The 2013 ICM criteria for defining Periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) can be remembered using the mnemonic below:
Mnemonic: 1 tract or 2 bact. and 3 of ABCDEF
1 sinus tract communication with the joint OR
2 positive periprosthetic cultures with phenotypically identical bacteria
AND
3 of the following six minor criteria:
a. Acute phase reactants: CRP >10 mg/L and ESR >30 mm/hr
b. Biopsy of periprosthetic tissue: >5 neutrophils/hpf in 5 high power fields
c. Culture positive: Single
d. Differential count in synovial fluid: >80% PMN
e. Esterase: Leukocyte esterase ++
(2011 MSIS criteria uses purulence in the affected joint as a minor criterion insted of leukocyte esterase and would require 4 out of six insted of 3 out of six minor criteria for diagnosis)
f. Full count in synovial fluid: >3000 WBC/microlitre
The 2018 PJI definition is based on scoring system and is diagnosed with score of 6 or more preoperatively or intraoperatively. The new 2018 definition of PJI is available here: https://josr-online.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13018-019-1185-y/tables/1
Trampuz and Zimmerli classifies PJI as:
- Early: Upto 3 months postoperatively
- Delayed: 3-24 months from index surgery
- Late: After 24 months from index surgery
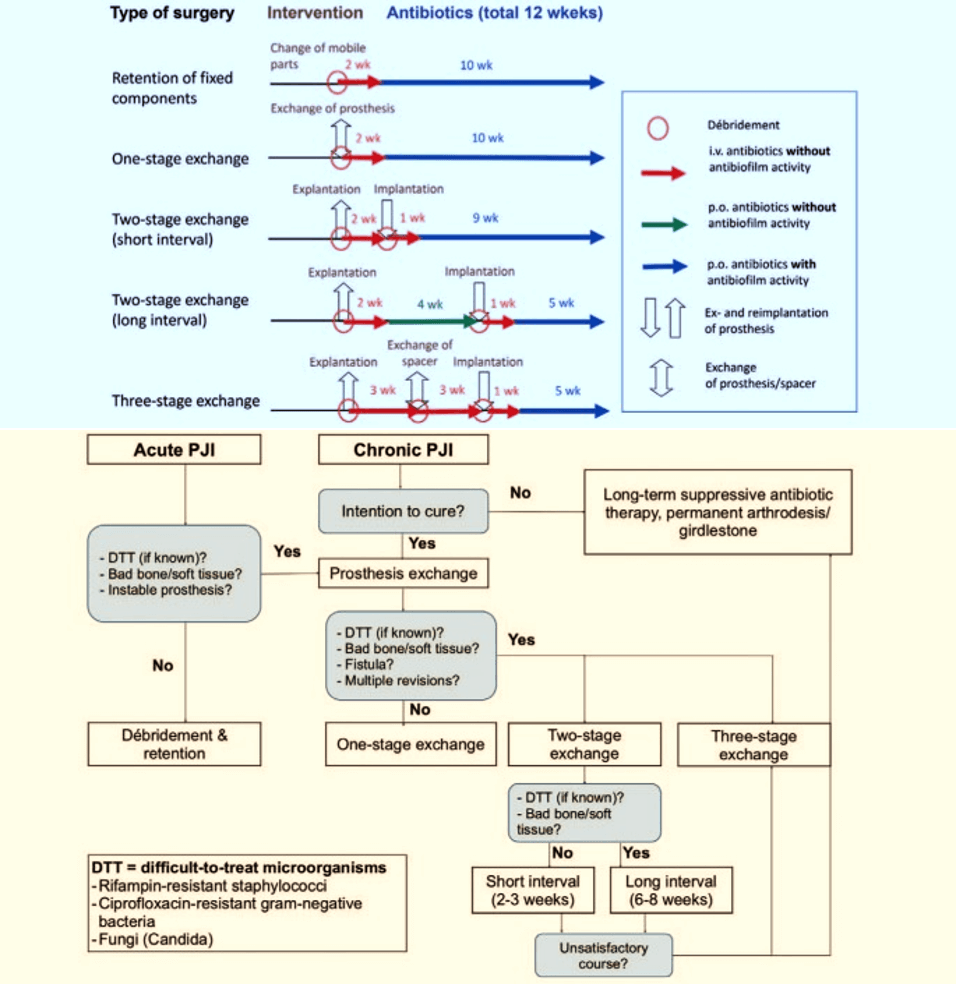
Another classification of PJI:
| Acute PJI | Chronic PJI | |
| Pathogenesis | ||
| a. Perioperative | <4 weeks after surgery (early) | ≥4 weeks after surgery (delayed/low-grade) |
| b. Hematogenous or per continuitatem | <3 weeks of symptom duration | ≥3 weeks of symptom duration |
| Clinical features | Acute pain, fever, red/swollen joint, prolonged postoperative discharge (7-10 days) | Chronic pain, loosening of prosthesis, sinus tract (fistula) |
| Biofilm | Immature | Mature |
| Causative organism | Highly virulent: Staphylococcus aureus, gram negative bacteria (E.coli, Klebsiella, Pseudomonas) | Low virulent: Coagulase negative staphylococci (Staph. epidermidis), Cutibacterium acnes |
| Surgical treatment | Debridement and retention of prosthesis (change of mobile parts) | Complete removal of prosthesis (exchange in 1 or 2 stages) |
Examples of biofilm active antibiotics:
- Gram positive organisms: Rifampicin
- Gram negative rods: Ciprofloxacin
These should be reserved for the period after implantation of the definitive implant.
Reference:
1. Guan, H., Fu, J., Li, X. et al. The 2018 new definition of periprosthetic joint infection improves the diagnostic efficiency in the Chinese population. J Orthop Surg Res 14, 151 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-019-1185-y
2. Li, C., Renz, N., Trampuz, A. et al. Twenty common errors in the diagnosis and treatment of periprosthetic joint infection. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 44, 3–14 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-019-04426-7