1. Para-aortic (lumbar) nodes: Gonads (derive blood supply from kidneys)
- Male: Testis, Epididymis
- Female: Ovaries, Fallopian tube (except isthmus and intra-uterine parts), Uterine fundus
2. Inferior mesenteric nodes: As of blood supply – to the structures derived from hindgut
- Descending colon
- Sigmoid colon
- Superior-most rectum
3. Common iliac nodes: Receives external and internal iliac nodes; Drains into para-aortic nodes
4. Superficial inguinal nodes: Everything that can be touched with fingers with few exceptions:
- Posterolateral part of calf (can be touched) – but drains to popliteal nodes
- Glans clitoris and Glans penis with distal spongy urethra (can be touched) – but drains to deep inguinal nodes
- Round ligament and cornu of uterus (cannot be touched) – but drains to superficial inguinal nodes
Hence, the drainage area is –
- Skin below umbilicus including scrotum, vulva and perianal skin with exceptions
- Anal canal below pectinate line
- Vagina inferior to hymen
- Round ligament and cornu of uterus (exception)
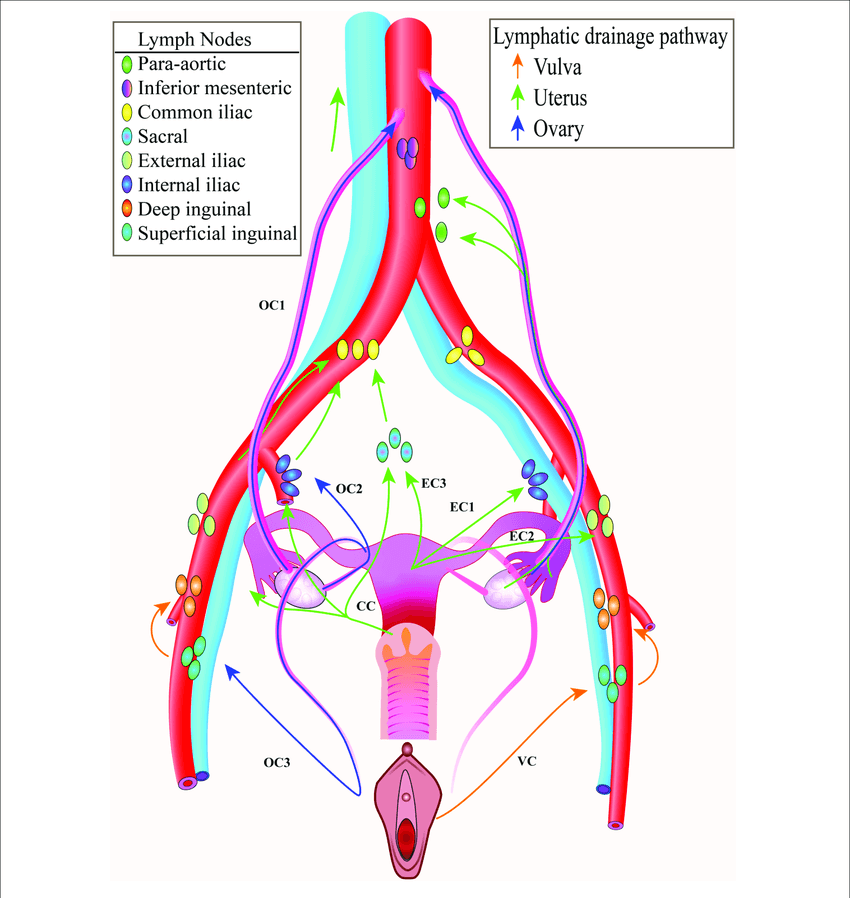
5. Deep inguinal nodes: Glans clitoris, Glans penis and distal spongy urethra
6. Internal iliac nodes: All pelvic viscera, deep parts of perineum, gluteal muscles and posterior thigh with few exceptions:
- Superior bladder
- Superior pelvic ureter
- Superior vagina, cervix and lower uterine body
- Seminal gland, Ductus deferens (pelvic part), Spongy and intermediate urethra
- Superior parts of rectum
Hence, the drainage area is –
- Base of bladder + Prostate and prostatic urethra
- Lower pelvic ureter
- Inferior rectum and anal canal above pectinate line
- Body of uterus, cervix, upper and middle vagina
- Inferior seminal glands, cavernosus bodies
7. External iliac nodes: Antero-superior pelvic structures
- Superior bladder
- Superior pelvic ureter
- Lower body of uterus, Cervix and Upper vagina
- Seminal gland, Ductus deferens (pelvic part), Intermediate and spongy urethra
7. Sacral nodes: Postero-inferior pelvic structures, Inferior rectum, Inferior vagina
8. Para-rectal nodes: Superior rectum