Anatomy of Vertebral Pedicle
Width (narrowest transverse diameter):
- Narrowest at T4-T5 (4-5 mm)
- Above and below this level, the width gradually increases to almost double at T1 and T11 (8 mm)
- Narrowest for lumbar at L2 (two for tiny; 2 X 3 = 6 mm)
- Increases gradually to L5 (5 X 3 = 15 mm)
Height (narrowest sagittal diameter):
- Narrowest at T1 (8 mm; T1 pedicle is like a square)
- Gradually increases downwards and is almost double at T12 (16-17 mm)
- Lumbar region i.e. L2-L5 (15 mm)
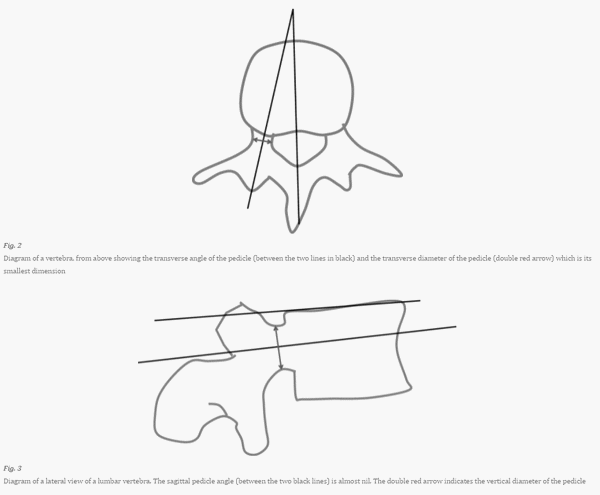
Sagittal or Craniocaudal angle (obliquity in the sagittal plane between the axis of the pedicle and the superior endplate of the vertebra):
- T1-T11 (15-20 degrees caudad)
- T12-L1 (5 degrees caudad)
- L2-L5 (almost parallel to the superior endplate, i.e. ~0 degrees)
Coronal, Transverse or Mediolateral angle (obliquity in the transverse plane between the axis of the pedicle and the anteroposterior axis of the vertebra):
- Narrowest at T11-L1 (~5 degrees medial)
- Increases as we go up to T1 (25 degrees medial)
- Increases 5 degrees with each vertebra as we go downwards from L1 to L5 (25 degrees medial)
- L1: 5 degrees
- L2: 10 degrees
- L3: 15 degrees
- L4: 20 degrees
- L5: 25 degrees
- S1: 30 degrees
Entry point of Pedicle Screw
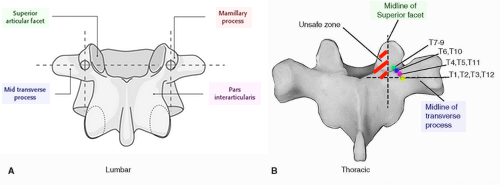
Thoracic spine
Safe zone: Lateral to the midpoint of superior facet and Proximal to the midpoint of transverse process
In the thoracic spine, transverse process commonly does not align with the pedicle in the axial plane. Thus, the anatomic landmarks that are used for lumbar pedicle screw insertion cannot be reliably used in the thoracic spine. The transverse process is rostral to the pedicle in the upper thoracic spine and caudal to the pedicle in the lower thoracic spine (crossover occurs at T6-7).
Mnemonic: 7,8,9 on the line
| Entry point | Progression | Vertebrae in ascending order | Vertebrae in descending order |
| Line with superior border of transverse process – Lateral to midpoint of superior articular facet | Most cranial and medial | T7, T8 | T9 |
| Line with junction of superior border and upper 1/3rd of transverse process – Lateral to midpoint of superior articular facet | More caudal and lateral | T6 | T10 |
| Line with upper 1/3rd of transverse process – Lateral to midpoint of superior articular facet | More caudal and lateral | T5, T4 | T11 |
| Line with midpoint of transverse process – Transverse process/Lamina junction | Most caudal and lateral | T1, T2, T3 | T12 |
Lumbar spine
1. Intersection technique (most commonly used): Lateral aspect of facet joint and midpoint of transverse process
2. Pars-interarticularis technique (medial to intersection technique)
3. Mamillary process technique (lateral to intersection technique)
Gearshift technique
To avoid medial wall penetration, the gearshift (2 mm blunt-tipped pedicle finder) is initially pointed laterally when the pedicle is entered.
Direction of Pedicle Screw
Medial to medial wall of pedicle: Dural sac
Inferior to medial wall of pedicle: Nerve root in neural foramen
Ventral penetration of Screw
80% of vertebral body

He is the section editor of Orthopedics in Epomedicine. He searches for and share simpler ways to make complicated medical topics simple. He also loves writing poetry, listening and playing music. He is currently pursuing Fellowship in Hip, Pelvi-acetabulum and Arthroplasty at B&B Hospital.