Definition
Mubarak and Hargens (1981) defined compartment syndrome as an elevation of the interstitial pressure in a closed osseofascial compartment that results in microvascular compromise.
Pathophysiology
Tissue perfusion = Capillary perfusion pressure – Interstitial fluid pressure
- Normal capillary pressure at rest: 20-33 mmHg (approximately 25 mmHg)
- Normal interstitial fluid pressure at rest: 10 mmHg
3 major theories for microvascular dysfunction and ischemia:
- Critical closing pressure theory:
- Transmural pressure = Intravascular pressure – Tissue pressure
- Transmural pressure drops to ‘critical pressure’ → Active closure of small arterioles
- Microvascular occlusion theory:
- Compartment pressure above this level (absolute compartment pressure) → Compartment syndrome
- Arteriovenous (AV) gradient theory:
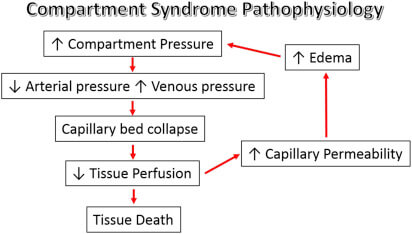
- Increase in tissue pressure → Decreased AV pressure gradient → Reduction of blood flow
Tissue survival:
- Muscle
- 3-4 hrs: Reversible changes
- 6 hrs: Variable damage
- 8 hrs: Irreversible changes
- Nerve
- 2 hrs: Loose nerve conduction
- 4 hrs: Neuropraxia
- 8 hrs: Irreversible changes
Vicious cycle of compartment syndrome:
Reperfusion injury: Since the tissue pressure does not exceed the systolic blood pressure, there is the potential for some continued perfusion in the affected compartment. This leads to reperfusion injury and includes the release of reactive oxygen metabolites as well as pronounced neutrophil activation.