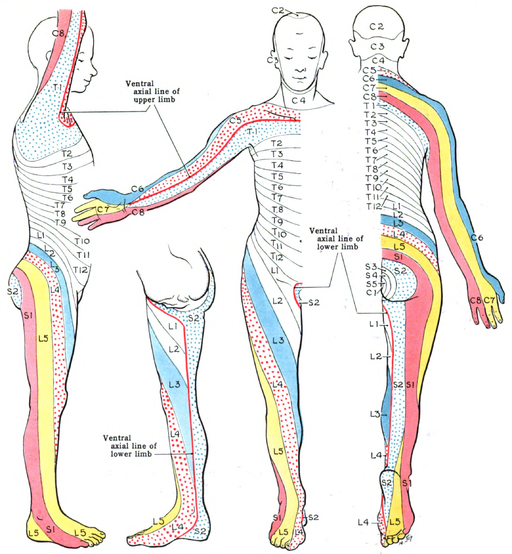
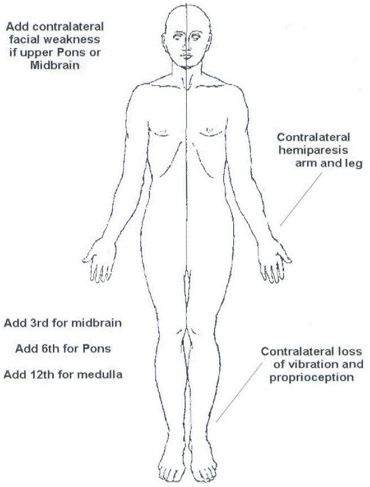
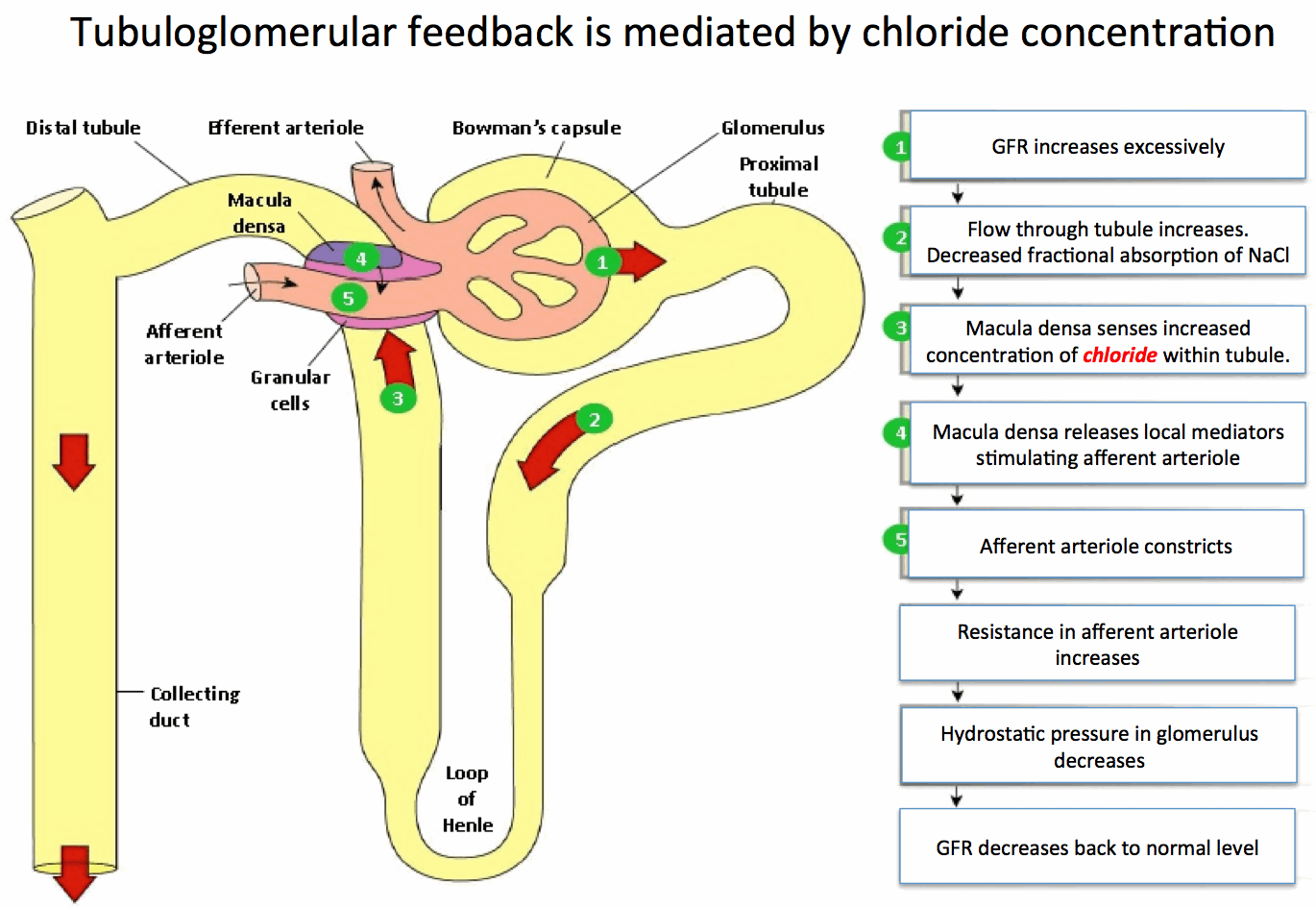
Pathology Spotter Series: Instruments
Level: Undergraduate (MBBS)
A) Spotter 1:

Instrument: Paraffin Block
Use: Tissue embedding – After adding fixative, biopsies are embedded in paraffin/wax to support the tissue so that thin sections or slices can be cut and placed on a microscope slide.
B) Spotter 2:
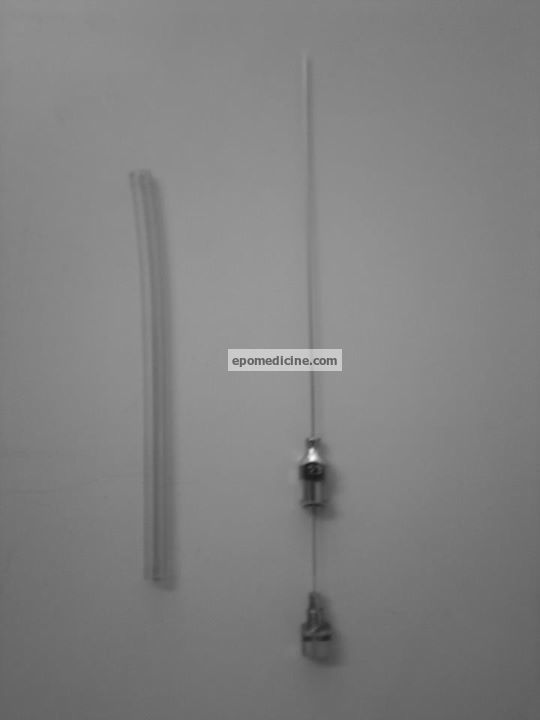

Instrument: Lumbar Puncture Needle
Uses:
- Collect CSF sample (spinal tap) for biochemical, microbiological and cytological analysis
- Spinal anesthesia
- Therapeutic lumbar puncture (to relieve increased ICP)
Site of insertion: Between L3 and L4 in adults
C) Spotter 3:

Instrument name: L-mold
Use: Tissue embedding – tissue is embedded to make tissue block used to prepare paraffin blocks.
D) Spotter 4:

Instrument name: Bone Marrow Aspiration Needle
Sites of bone marrow aspiration:
- Posterior iliac crest
- Anterior superior iliac crest
- Sternum (last resort in morbid obese and older than 12 years)
- Tibia (Only in infants younger than 1 years)
Indications of Bone marrow aspiration:
- Unexplained anaemia, abnormal red cell indices, cytopenias or cytoses
- Abnormal peripheral blood smear morphology suggestive of bone marrow pathology
- Diagnosis, staging and follow-up of malignant haematological disorders (e.g. acute and chronic leukaemias,myelodysplastic syndromes, chronic myeloproliferative disorders, lymphomas, plasma cell myeloma, amyloidosis, mastocytosis)
- Suspected bone marrow metastases
- Unexplained focal bony lesions on radiological imaging
- Unexplained organomegaly or presence of mass lesions inaccessible for biopsy
- Microbiological culture for investigations of pyrexia of unknown origin or specific infections, e.g. military tuberculosis, leishmaniasis, malaria
- Evaluation of iron stores
- Investigation of lipid/glycogen storage disorders
- Exclusion of haematological disease in potential allogeneic stem cell transplant donors
E) Spotter 5:

Instrument name: Tissue cassettes
Use: Tissue processing – these cassettes are totally resistant to most reagents and their slots offer maximum flow through for good fluid exchange and proper drainage.