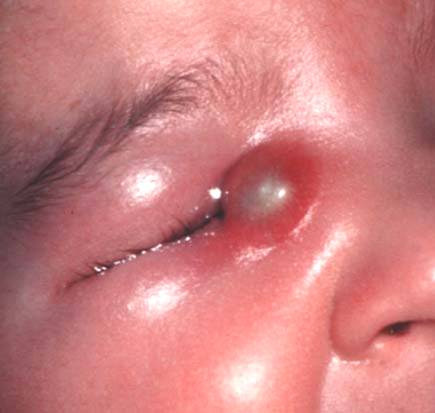
Definition: Acute dacryocystitis is the inflammation of the lacrimal sac which usually occurs in very young children or > 40 years
Microbiology of Acute Dacryocystitis:
- Congenital: Hemophilus influenzae (acute – rare), Others (chronic)
- Adults:
- Acute: Staphylococcus aureus, Beta-hemolytic streptococci
- Chronic: Streptococcus pneumoniae, Candida albicans
Etiology of Acute Dacryocystitis:
1. Congenital: Nasolacrimal duct obstruction –
- Membranous: valve of Hasner
- Epithelial debris
- Complete non-canalization
2. Adult:
a. Acute:
- Exacerbation of chronic dacryocystitis
- Acute peridacryocystitis (neighboring structures): Paranasal sinus, bones, dental abscess, caries teeth
b. Chronic:
- Anatomical: narrow bony canal, partial canalization, excessive folds
- Foreign body
- Hyperlacrimation (stagnation of tears)
- Recurrent conjunctivitis
- Lower end Nasolacrimal duct obstruction: Polyps, Hypertrophied turbinates, Deviated nasal septum, tumors, atrophic rhinitis
Clinical features of Acute Dacryocystitis:
A. Congenital:
- Epiphora and Discharge (usually after 7 days of birth)
- Regurgitation test positive
- Swelling in lacrimal sac area
B. Acute:
- Stage of Cellulitis: Signs of inflammation in sac area, epiphora, fever, malaise
- Stage of Lacrimal abscess: Fluctuant swelling, pus point (below and outer side)
- Stage of Fistula formation: below medial palpebral ligament
C. Chronic:
- Catarrhal stage (mild inflammation): epiphora +/- mild redness in sac area
- Regurgitation test: clear fluid or few fibrinous mucoid flakes
- Stage of lacrimal mucocele: epiphora + swelling in sac area
- Regurgitation test: milky/gelatinous mucoid fluid
- Stage of Suppurative dacryocystitis (pyogenic infection): mucocele → pyocele, epiphora, recurrent conjunctivitis, swelling, redness
- Regurgitation test: Frank purulent discharge
- Stage of fibrotic sac: persistent epiphora and discharge
Complications of Acute Dacryocystitis:
A. Acute dacryocystitis:
- Acute conjunctivitis
- Corneal abrasion/ulcer
- Lid abscess
- Osteomyelitis of lacrimal bone
- Orbital cellulitis
- Rarely, Cavernous sinus thrombosis and septicemia
B. Chronic dacryocystitis:
- Chronic conjunctivitis
- Simple corneal abrasion/ulcer
- Lid: Ectropion, Eczema, Maceration
- Acute on chronic dacryocystitis
- Endophthalmitis (Intraocular surgery)
Treatment of Acute Dacryocystitis:
A. Congenital:
- 6-8 weeks age: Massage over lacrimal sac + Topical antibiotics
- 2-4 months age: Lacrimal syringing with normal saline X 1 or 2 times per week + Antibiotics
- 4-6 months age: Probing of Nasolacrimal duct under GA with Bowman’s probe every month
- Probing failure: Silicone tube intubations
- > 4 years with failed probing: Dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR)
B. Acute adult:
- Cellulitis: Antibiotics (Systemic + Topical), NSAIDs, hot fomentation
- Lacrimal abscess: Incision and Drainage +/- Dacryocystorhinectomy (DCT) or DCR
- Fistula: Antibiotics, fistulectomy + DCT or DCR
C. Chronic adult:
- Conservative: repeated lacrimal syringing
- Surgical: DCR, DCT, conjunctivo-DCR
Criggler’s massage:
- Indication: Congenital Nasolacrimal duct obstruction
- Principle: Massaging lacrimal sac in an inferior direction to increase the hydrostatic pressure in nasolacrimal duct to force it open.
- Frequency: 10 times in a episode X 3 times/day