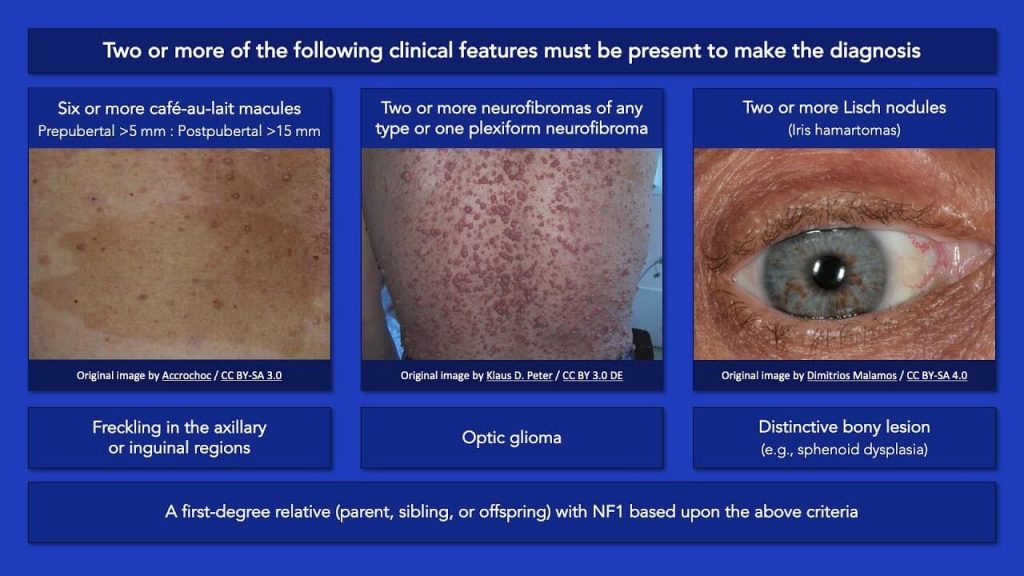
Mnemonic: 2 out of ABCDEFG
1. Axillary or inguinal freckling
2. Bone lesions (sphenoid dysplasia, tibial pseudoarthrosis)
3. Cafe au lait macules/spots (>/= 6 in number; >/= 5 mm in prepubertal and >/= 15 mm in postpubertal)
4. Dermatologic neurofibroma
5. Eye hamartomas/Lisch nodules >/= 2
6. Family history (first degree relative)
7. Glioma of optic nerve
The diagnosis of NF1 requires atleast 2 of 7 NIH criteria.