You must have seen the statement in First Aid that says – low serum magnesium causes increase in Parathyroid hormone secretion and very low serum magnesium causes decrease in Parathyroid hormone secretion. Doesn’t this make you curious? Let’s explore the underlying mechanism in depth.
How Calcium and Magnesium Mediated PTH Feedback Inhibition Works ?
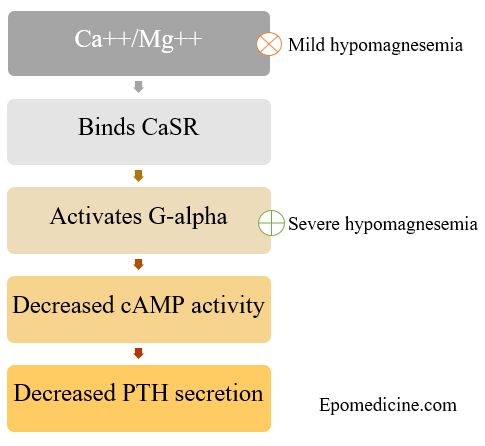
1. Both the divalent cations (Ca++ and Mg++) act on the same negative feedback receptor on parathyroid chief cells.
2. Extracellular magnesium is a direct agonist of the CaSR (Calcium Sensing Receptor) with a potency of 2-3 times less than that of calcium.
3. Increased Magnesium and calcium leads to increased binding of divalent cations with CaSR which activates the G-alpha subunit (both q and i) leading to decreased cAMP activity.
4. Hence, PTH release is inhbited.
Why PTH release increases in Mild hypomagnesemia ?
- Seen in magnesium level as low as 0.5 mmol/L.
- Decrease in extracellular Magnesium leads to decreased CaSR activation.
- This leads to decreased feedback inhibition of PTH and hence, increased PTH secretion.
Why PTH release decreases in Severe hypomagnesemia?
- Seen in magnesium level <0.5 mmol/L.
- Magnesium binding site responsible for inhibition of PTH secretion is not identical with the extracellular binding site of the CaSR.
- Intracellular magnesium depletion leads to decreased magnesium binding to G-alpha subunit associated with CaSR.
- This leads to disinhibition of G-alpha subunit which mimicks CaSR activation.
- This leads to decreased PTH release (not decreased PTH synthesis).
This effect is called paradoxical block of PTH secretion.
Conclusion:
1. Mild hypomagnesemia → Decreased extracellular Mg++ → Decreased feedback inhibition → ↑PTH secretion
2. Severe hypomagnesemia → Decreased intracellular Mg++ → Removal of CaSR associated G-alpha disinhibition → ↓PTH secretion
References:
- Immunoendocrinology: Scientific and Clinical Aspects edited by George S. Eisenbarth
- Hypoparathyroidism edited by Maria Luisa Brandi, Edward Meigs Brown