Antitubercular drug symbols
- H = Isoniazid
- R = Rifampicin
- Z = Pyrazinamide
- E = Ethambutol
- S = Streptomycin
- Km = Kanamycin
- Cm = Capreomycin
- Lfx = Levofloxacin
- Ofx = Ofloxacin
- Mfx = Moxifloxacin
- Eto = Ethionamide
- PAS = Para-aminosalicylic acid
- Cs = Cycloserine
- Amx/Clv = Amoxicillin-Clavulanate
- Bdq = Bedaquiline
- Lzd = Linezolid
- Imp/Clv = Imipenem-Clavulanate
- Dlm = Delaminid
Xpert MTB/Rif can detect TB and rifampicin resistant TB and provide results within 2 hours. Whenever available, it is used as a first-line diagnostic tool for all presumptive TB cases and where not available, it should be performed in following groups:
- All re-treatment cases including failure, relapse and loss to followup
- Symptomatic contacts of DR TB
- Non-converters by month 2 or subsequent followup
- Symptomatic contacts of Pulmonary Bacteriologically Confirmed (PBC) TB
- People diagnosed with or living with HIV
- Health Care Workers
- Children (age less than or equal to 14 years)
- Patients from congregate settings (prisons, hostels, etc.)
- New patients of high risk groups such as uncontrolled Diabetes and other immunocompromised conditions
- Extrapulmonary (EP) samples
- Sputum smear-negative patients with clinical or radiological suspicion for TB
Line Probe Assay (LPA): First (1st) line LPA includes INH and Rifampicin susceptibilities and Second (2nd) line LPA includes Fluoroquinolones and injectable anti TB drugs (aminoglycosides and polypeptides) susceptibilities. It is to be performed in cases of:
- Rifampicin resistance is detected in Xpert/Rif (these patients should also get culture drug sensitvity testing/DST done)
- All Retreatment patients (including failure, loss to follow up and relapse)
- Non-converters by month 2 or subsequent follow-up
- Not getting better/getting worse during the continuation phase of the first line treatment
Treatment regimens in retreatment cases:
- H and R sensitive: 2HRZE + 4HR
- H resistance and R and FQ sensitive: 6HRZE + Lfx
- R resistance and H sensitivity status unknown: 6HRZE
- R sensitive and H and FQ resistance: 6(H)RZE
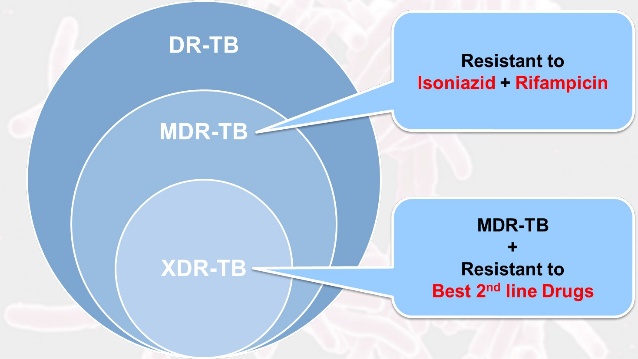
RR TB and Multiple Drug Resistance Tuberculosis (MDR TB)
Definition: MDR tuberculosis is defined as resistance to minimum of H and R.
Shorter Standardized Treatment Regimen (SSTR): If FQ and SLI (Second line injectable) sensitive
- 4-6 (E-Cfz-Z-Eto-Mfxₕ-Am-Hₕ) / 5 (E-Cfz-Z-Mfxₕ)
*ₕ = high dose
Mnemonic: ECZEMA Hydrocort
E-Cfz-Z and Mfx is used in both intensive and continuation phase.
Long Regimen 1 (LR1): If FQ resistant and SLI sensitive
- Bdq(6), 18 Lfx-Lzd-Cfz-Z
Long Regimen 2 (LR2): If FQ sensitive and SLI resistant
- Bdq (12), 18 Lzd-Cfz-Cs-Z
Extreme Drug Resistance Tuberculosis (XDR TB)
Definition: XDR tuberculosis is defined as resistance to H and R, all fluoroquinolones and atleast one injectable agent.
Long regimen 4 (LR4) for XDR TB:
- Dlm(12), Imp/Clv (10), 18 Cs-Eto-PAS-Cfz-Z
Reference:
National Guidelines on Drug Resistant Tuberculosis Management (2019, Nepal)