Synonyms: Monoclonal spike, M-protein spike, Monoclonal band, Monoclonal gammopathy
Tests showing M-spike
- Serum Protein Electrophoresis (SPEP)
- Urine Protein Electrophoresis (UPEP)
Normal SPEP or UPEP
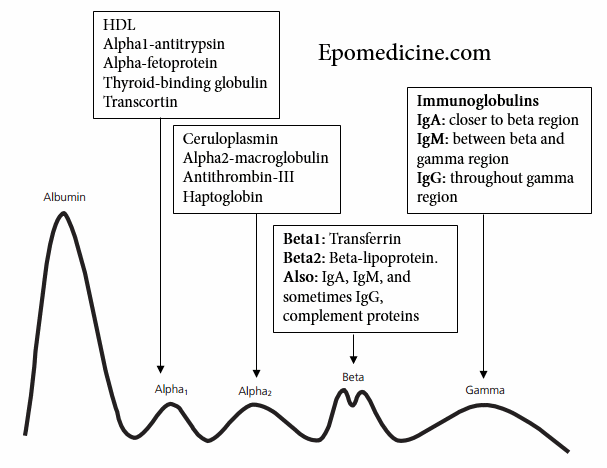
Electrophoresis is a method of separating proteins based on their physical properties. Albumin – the largest peak, lies closest to the positive electrode and the next five components (globulins) labeled alpha1, alpha2, beta1, beta2, and gamma lie toward the negative electrodes with gamma being closest.
The contents of the various components are given in the picture below:
The region for CRP and fibrinogen are between beta and gamma components.
Gamma component of SPEP and UPEP
Focus upon components other than gamma region is beyond the scope of this post. Gamma region comprises of immunoglobulins – predominantly IgG.
Decreased gamma globulins:
- Agammaglobulinemia
- Hypogammaglobulinemia
Increased gamma globulins:
- Amyloidosis
- Chronic infections (granulomatous diseases)
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)
- Cirrhosis
- Hodgkin’s disease
- Malignant lymphoma
- Multiple myeloma
- Rheumatoid and collagen diseases
- Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia
M-spike
An M-spike is characterized by the presence of a sharp, well-defined band with a single heavy chain and a similar band with a kappa or lambda light chain and indicates monoclonal gammopathy.
A polyclonal gammopathy is characterized by a broad diffuse band with one or more heavy chains and kappa and lambda light chains.
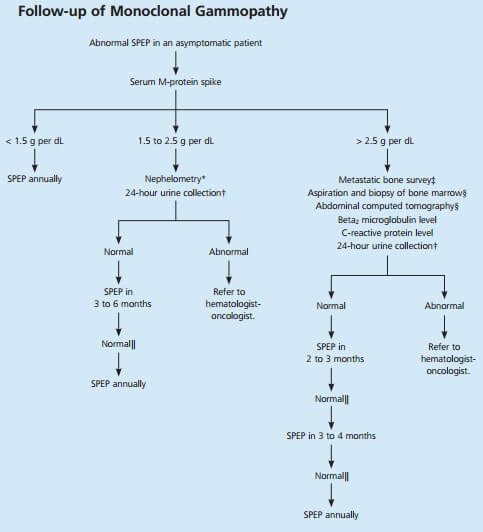
Once an M-spike is identified, multiple myeloma may be differentiated from MGUS:
1. Multiple myeloma: M-protein is usually >3 g/dl.
2. Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS): M-protein is usually <3 g/dl
M-spike absent in SPEP but present in UPEP
SPEP detects the M-protein and UPEP detects a light chain predominance. Some light chains are freely filtered in the glomerulus and quickly cleared from blood. They are called light chain secretors who comprise around 20% of the multiple myeloma. In such cases, SPEP cannot identify the light chains and UPEP will increase the sensitivity of identifying the myeloma protein when combined with SPEP from 80 to 95%.
Next test to order – Immunofixation
Immunofixation confirms that the component is monoclonal and identifies immunoglobulin type. In multiple myeloma:
- IgG (50%) > IgA (20%) > IgD (2%) > IgM (0.5%)
- Light chain only (20%)
There’s a possibility that a patient of multiple myeloma may sometimes have hypoalbuminemia and hypogammaglobulinemia. Rarely, M-spike may be present in beta or alpha-2 region which may go undetected with SPEP and UPEP. This is where Immunofixation comes handy. When clinical suspicion is high, but SPEP and UPEP are non-diagnostic, immunofixation must be ordered.
Recommended reading: Quick approach to Multiple Myeloma
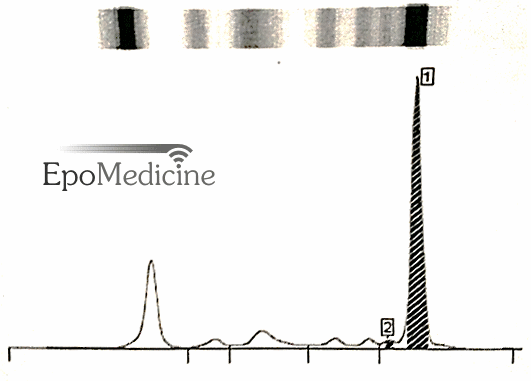
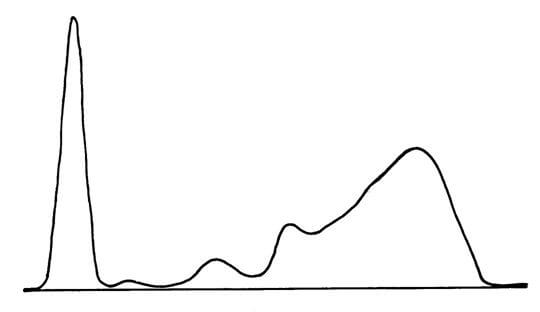
M-spike presentation:
This is a nice cursory outline but why does it not include Bence-Jones protein?
Thank you