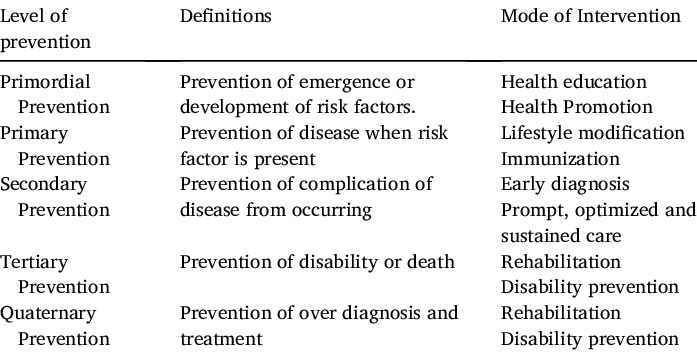
| Level | Mnemonic | Target population | Goals | Mode of intervention |
| Primordial | Prevent risk factors | General population | Prevent emergence of risk factors | Health education Health promotion |
| Primary | Prevent disease | General population | Prevent disease onset | Lifestyle modification Immunization |
| Secondary | Screening | Subclinical (asymptomatic) | Prevent symptom onset | Early diagnosis Prompt optimized & sustained care |
| Tertiary | Treatment | Clinical (symptomatic) | Prevent clinical disease progression & complications | Rehabilitation Disability prevention |
| Quarternery | Quit unnecessary treatment | Symptomatic patients but overmedicalized or not treatable | Prevent overtreatment & iatrogenic harm | Rehabilitation Disability prevention |
Example
For Diabetes mellitus:
- Primordial prevention: Health education about diabetes mellitus
- Primary prevention: Healthy diet and exercise to prevent diabetes onset in future
- Secondary prevention: Glucose screening for type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Tertiary prevention: Use medications to treat previously diagnosed diabetes
- Quarternery prevention: Discontinue sulfonylurea after multiple hypoglycemic episodes