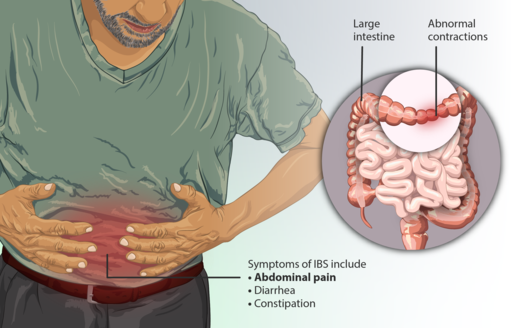
Rome IV Criteria for IBS
Mnemonic: 1, 2, 3
Recurrent abdominal pain on average:
- ≥1 day/week associated with
- ≥2 of the following in
- last 3 months:
- Related to defecation
- Associated with a change in stool frequency
- Associated with a change in stool form (appearance)
Criteria fulfilled for the last 3 months with symptom onset at least 6 months prior to diagnosis
Alarm findings (Red flags)
Mnemonic: ALARMING
- Age 50 or more
- Loss of weight (unintentional), Lymphadenopathy
- Anemia
- Recent change in bowel habit
- Mass (abdominal)
- Intestinal bleeding (melena, hematochezia, FOBT positive)
- Night diarrhea
- Genealogy (family) history of Colon carcinoma, Inflammatory Bowel Disease or Celiac disease
Additional diagnostic testing
Mnemonic: Rule out 4 “C”
1. Carcinoma
2. Celiac disease
3. Colitis
4. Carbohydrate (lactose) intolerance
Additional diagnostic testing is not indicated if the patient meets the Rome IV diagnostic criteria in the absence of alarm features. Some recommended additional diagnostic tests are:
- All patients ≥ 50 years old or those with alarm features: Colonoscopy for Colorectal carcinoma screening
- IBS with Diarrhea or Mixed: Serologic tests for celiac disease
- IBS with Diarrhea: Colonoscopy with random biopsies (to rule out microscopic colitis)
- When no response to diet and still suspicious: Breath testing for lactose intolerance
Management
Mnemonic: BCDEF
1. Cognitive Behavioral therapy
2. Drugs:
| Constipation predominant | Diarrhea predominant | |
| 1st line | Constipation: Osmotic laxatives Pain: Antispasmodics | Diarrhea: Loperamide, Cholestyramine (Bile acid sequestrants) Pain: Antispasmodics |
| 2nd line | Secretagogues: Linaclotide Lubiprostone | Rifaximin Low dose TCA Eluxadoline (mixed opioid receptor agonist) |
| 3rd line | Tegaserod (Serotonin-4 agonist) | Alosetron (Serotonin-3 antagonist) |
3. Education and reassurance (most important)
4. Food modifications:
- Lactose restriction
- Gluten restriction
- Fiber supplementation
- Low-FODMAP diet
Genius 🙏🏾🙏🏾🙏🏾🙏🏾. Awesome. I will keep praying for you man. This is Gold 👏👏👏