HIV Replication and Antiretroviral Mechanism of Action
Mnemonic: AFRITAB
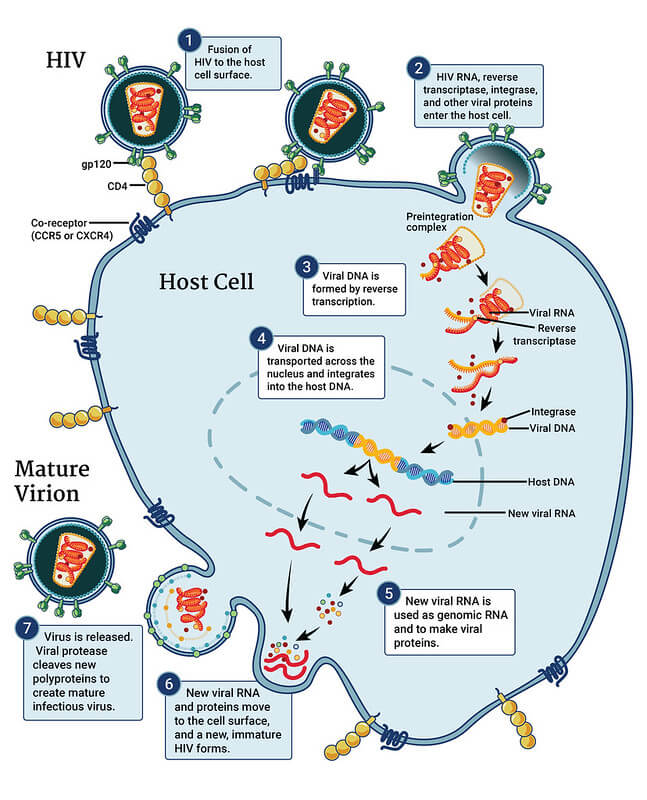
1. Attachment (to CD4 cells)
- gp120 (virus) + CD4 receptor + co-receptor on CD4 cells (CCR5 in R5-tropic; CXCR4 in X4-tropic)
- CCR5 inhibitor: Maraviroc
2. Fusion (enters CD4 cells and dump it’s contents – RNA and reverse transcriptase)
- Fusion inhibitor: Enfuviritide (Mnemonic: Envelope protein gp41 binding to inhibit fusion)
3. Reverse transcription (1 strand RNA becomes 2 strand DNA)
- Nucleotide/Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NRTIs): Abacavir, Tenofovir, Lamivudine, Emtricitabine, Zidovudine, Didanosine
- Competitive inhibitor
- Mnemonic: Ends in “vir” or “ine”
- Non-Nucleotide Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NNRTIs): Efavirenz, Nevirapine, Dapivirine, Delaviridine, Rilpivirine, Etravirine
- Non-competitive inhibitor
- More specific than NRTI
- Mnemonic: “vir” in the middle of name
4. Integration (HIV DNA integrates into human’s CD4 cell’s DNA)
- Integrase inhibitors (INSTI): Raltegravir, Dolutegravir, Elvitegravir, Bictegravir
- Mnemonic: “tegravir”
5. Transcription (long chains of RNA and proteins containing information to make new HIV is released)
6. Assembly (protease breaks these long chains into “packages” that lineup along the edge of CD4 cell)
- Protease inhibitors (PI): Ritonavir, Indinavir, Nelfinavir, Saquinavir, Atazanavir, Darunavir, Fosamprenavir, Tipranavir
- Mnemonic: “navir”
7. Budding (newly formed HIV along the cell wall pushes itself out of CD4 cell, stealing a part of the cell’s protective coating)
Pharmacokinetic enhancers: Inhibit CYP3A4 and increase drug levels:
- PI and Booster: Ritonavir
- Booster alone: Cobicistat
Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy (HAART)
Indications:
- Symptomatic HIV disease (AIDS defining disease)
- Asymptomatic HIV disease with CD4 count:
- < 200/μl
- Decline of > 100 CD4 cells/μl per annum
- RNA level > 50,000 copies
Aim: HIV RNA level <50/μl
Regimens:
- PI sparing: 2 NRTI + 1 NNRTI (preferred)
- 2 NRTI + PI (preferred)
- 3 NRTI (only when NNRTI or PI cannot be used)
- NRTI + NNRTI + PI (advanced cases who have failed multiple previous regimens)
Drugs considered safe in pregnancy: Zidovudine, Lamivudine, Nevirapine, Nelfinavir, Saquinavir
Drug combinations to avoid:
| Combinations | Reasons to avoid |
| Zidovudine + Stavudine | Pharmacologic antagonism |
| Stavudine + Didanosine | Increased toxicity (lactic acidosis) |
| Lamivudine + Didanosine | Clinically not additive |
Post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP):
- Initiate within 72 hours (as early as possible)
- 2-3 HIV medications (3 medications preferred) taken every day for 28 days (4 weeks)
- Preferred: Tenofovir (TDF) + Emtricitabine (F) +/- Raltegravir or Dolutegravir
- Alternative: TDF + F + Darunavir + Ritonavir
Further reading: chw-04-hiv-life-cycle-meds.pdf (targethiv.org)