Plasma cell dyscrasia refers to an abnormal proliferation of plasma cells that usually secrete a monoclonal immunoglobulin.
A) CLINICAL FEATURES
Features vary among various conditions:
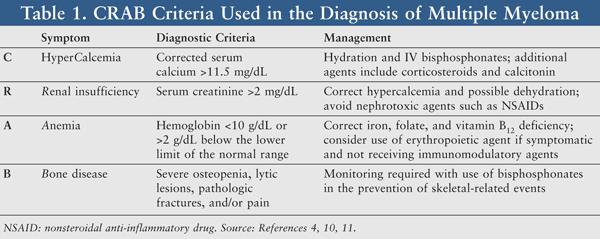
Mnemonic: CRAB Infection
1. Calcium increased:
- Hypercalcemia
- Nephrocalcinosis
and
Coagulopathy: Inhibition of or antibody against clotting factor; antibody-coated platelets
2. Renal failure or Renal Tubular Acidosis type II: Causes include –
- Bence-Jones Proteinuria
- Nephrocalcinosis
- Amyloidosis
- Hyperuricemia
- UTI
- Infiltration by myeloma cells
3. Anemia, Leukopenia, Thrombocytopenia
and
Amyloidosis
4. Bone:
- Swelling
- Pain
- Compression myelopathy
- POEMS syndrome: Polyneuropathy, Organomegaly, Endocrinopathy, M-protein, Skin changes
5. Infections: due to hypogammaglobulinemia
6. Hyperviscosity:
- Blurring of vision
- Headache
- Vertigo
- Nystagmus
6. Other: Peripheral neuropathy, Myelomatous meningitis
B) INVESTIGATIONS
- CBC: Pancytopenia, Increased ESR
- PBS: Rouleax formation
- Biochemistry profile:
- ↑ Calcium
- ↑ Urate
- Deranged RFT
- Electrolytes
- ALP ↑/=
- ↓ Protein; ↑ Albumin and ↓ Globulin
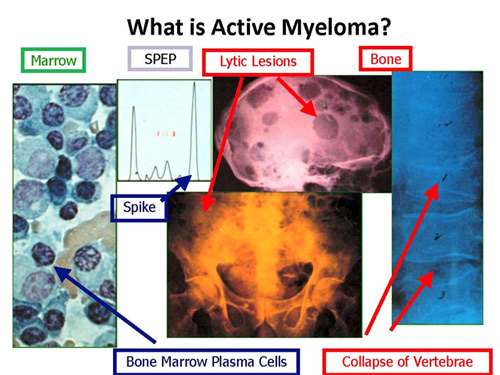
- Serum protein electrophoresis (SPEP): Quantifies M-protein (positive in 80%)
- Urine protein electrophoresis (UPEP): Detects 20% patients who are light chain secretors (BJ proteins)
- Immunofixation: Shows component is monoclonal and identifies immunoglobulin type –
- IgG (50%) > IgA (20%) > IgD (2%) > IgM (0.5%)
- Light chain only (20%)
- Non-secretors (1%) – plasma cells cannot excrete immunoglobulin molecule
- Serum free light chain assay: diagnosis and follow-up of treatment response
- β2 microglobulin and LDH: tumor burden
- Bone marrow biopsy:
- better prognosis = hyperdiploidy
- worse prognosis = deletion of chromosome 17p13 (10%) and certain translocations
- Skeletal survey: Plain radiographs to identify lytic bone lesions and pathological fractures; bone scan is not useful in diagnosing lytic lesions
C) DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA OF MULTIPLE MYELOMA
International Myeloma working group Diagnostic criteria: ≥2 of –
1. Asymptomatic:
- M-protein ≥ 3 gm/dl and/or
- Bone-marrow plasma cells ≥ 10%
2. Symptomatic: + ≥1 of CRAB
- Corrected Calcium ≥ 11.5 mg/dl
- Renal failure (Creatinine > 2 mg/dl)
- Anemia (Hb < 10 gm/dl)
- Bone (multiple lytic lesions/osteopenic)
D) VARIANTS
- 1 bone lesion, normal bone marrow, normal uninvolved immunoglobulins: biopsy shows solitary plasmacytoma
- Soft tissue mass (Upper respiratory tract, GI), No bone lesion, Normal bone marrow: Biopsy shows Extramedullary plasmacytoma
- No CRAB: Asymptomatic/Smoldering multiple myeloma
- Normal CBC and chemistries, Bone marrow ≤ 10% plasma cells, No lytic lesions, M component < 3 gm/dl, Normal uninvolved Immunoglobulins, Often normal UPEP: Monocloncal Gammopathy of Undetermined Significance (MGUS)
- Waldenstorm Macroglobulinemia:
- lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma (B-cell neoplasm secreting monoclonal IgM)
- like MGUS – no evidence of lytic bone lesions
- Fatigue (anemia)
- Tumor infiltration: bone marrow (cytopenia), hepatomegaly, splenomegaly
- Circulating monoclonal IgM: hyperviscosity, type I cryoglobulinemia (Raynaud’s phenomenon), platelet dysfunction (mucosal bleeding)
- IgM deposition: Amyloidosis, Glomerulopathy
- Autoantibody activity of IgM: chronic AIHA, neuropathy (IgM against myelin-associated glycoprotein)
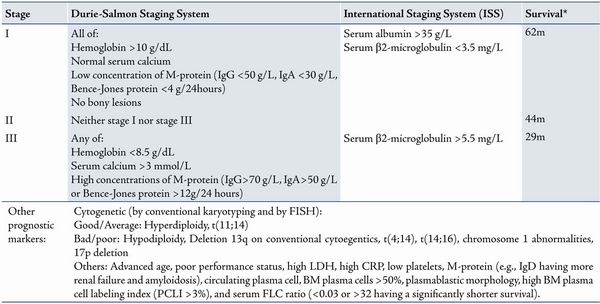
E) STAGING
Durie Salmon staging mnemonic: ABCdE
- Anemia: >10 to <8.5
- Bony lesions: <2 to Advanced
- BJ proteins (urine light chain): <4 gm/24 hr to >12 gm/24 hr
- Calcium degree: <12 to >12
- Electrophoresis:
- IgG: <5 to >7
- IgA: <3 to >5
F) TREATMENT
1. General treatment:
Plasmapheresis for hyperviscosity
2. Specific treatment:
a. Multiple myeloma: Chemotherapy ± Radiotherapy (for local problems) ± Autologous stem cell transplant (in <65 years without renal failure)
- Chemotherapy:
- Mephalan + Prednisolone X 6 wk pulses
- If cytopenic: IV cyclophosphamide weekly
- Fail/relapse: VAD (Vincristine, Adriamycin, Dexamethasone)
- Newer drugs: Thalidomide, Lenalidomide, Bortezomib
b. Solitary plasmacytoma: Radiotherapy <45 Gy; F/U with SPEP, IEP and UPEP
c. Extramedullary plasmacytoma: Radiotherapy
d. Asymptomatic/Smoldering multiple myeloma:
- Low risk features: Follow Up
- High risk features: Follow Up by Observation vs Chemotherapy
e. MGUS: Follow up with SPEP in 6 months and then yearly
f. Waldenstorm’s macroglobulinemia:
- Oral alkylating agents
- Newer therapies: Nucleoside analogs (fludarabine, cladribine), monoclonal antibodies (anti-CD20), thalidomide
- High dose chemotherapy followed by stem cell transplant for younger patients