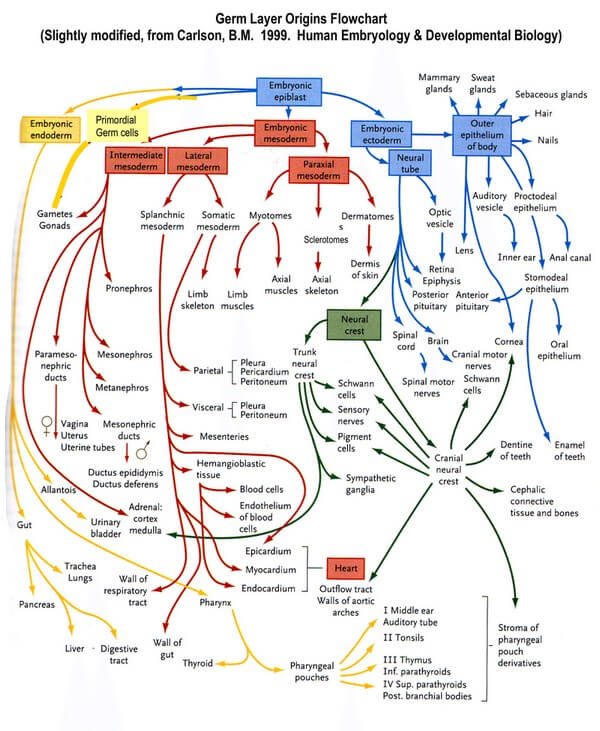
Principle of Germ Layer Segmentation
Ectoderm gives further rise to neuroectoderm and neural crest cells.
Endoderm remains intact.
Mesoderm gives further rise to paraxial mesoderm (somitomeres and 35 pairs of somites), intermediate mesoderm, and lateral mesoderm:
- The somites segment into the sclerotome (forms axial cartilage and bone), myotome (forms axial muscle), and the dermatome (forms the dermis of skin).
- The intermediate mesoderm forms the urogenital system.
- The lateral mesoderm is split into two layers by the formation of the intraembryonic coelom called the somatic layer and the splanchnic layer. The somatic layer of the lateral mesoderm and the ectoderm form the embryonic body wall or somatopleure. The visceral layer of the lateral mesoderm and the endoderm form the embryonic gut tube or splanchnopleure.
General Rule for Germ Layer Derivatives
Ectodermal derivatives:
1. Everything that makes you attractive: Skin, hair, nail, breasts, teeth enamel etc.
2. Nervous system: CNS, PNS, Sensory parts of eye, ear and nose
3. Epithelial linings that can be touched with your finger: Oral cavity, lower anal canal, external ear canal, terminal part of male urethra
4. Exocrine glands: Sweat, sebaceous, mammary, parotid, lacrimal, etc.
5. Heart: Aorticopulmonary septum and Endocardial cushion
Endodermal derivatives:
1. Lining of tube from nose, mouth and ear to anus and urethra and vagina except those that can be touched with your fingers.
2. Internal organs:
- Gastrointestinal tract: except spleen
- Renal and genitourinary system
Mesodermal derivatives:
1. All stuffs between skin and internal organs
2. Genitourinary and renal organs
3. Spleen
4. Adrenal cortex
5. Duramater
Derivatives of Ectoderm
a. Surface ectoderm:
- Skin
- Hair
- Nails
- Enamel of teeth
- Oral epithelium:
- Lip, cheeks, gums, part of floor of mouth
- Embryologic attachment with oral epithelium: Rathke’s pouch (Adenohypophysis)
- Lower third of anal canal below pectinate line
- Terminal (Glanular) part of male urethra
- Labia majora and outer surface of labia minora
- Epithelium of conjunctiva, cornea, ciliary body and iris
- External ear, outer layer of tympanic membrane and internal ear (sensory)
- Lens of eye
- Exocrine glands: Sweat, sebaceous, mammary, parotid, lacrimal, etc.
b. Neuroectoderm: CNS and brain
- Central Nervous System (CNS)
- Retina and Optic nerve
- Epithalamus (Pineal gland)
- Neurohypophysis
- Astrocytes
- Oligodendrocytes
- Ependymal cells
c. Neural crest: PNS and nearby non-neural structures
- Neuroendocrine:
- Adrenal medulla and chromaffin cells
- Enterochromaffin cells
- Parafollicular C cells of thyroid
- Melanocytes
- Ganglia: Sensory, cranial and autonomic
- Cranial nerves
- Celiac ganglion
- Schwann cells
- Meninges: Pia and arachnoid mater
- Pharyngeal arch chartilage
- Odontoblasts
- Aorticopulmonary septum
- Endocardial cushions
Ectodermal Derivative’s Mnemonic: 7 E
- Epidermis
- Epithelial linings of external orifices
- Ear, eye and nose – sensory part like olfactory epithelium, retina, etc.
- Enamel of teeth
- Exocrine glands
- Encephalon (CNS)
- Eye lens
Derivatives of Mesoderm
- Connective tissues:
- Loose areolar tissue
- Superficial and deep fascia
- Ligaments
- Tendons
- Aponeuroses
- Dermis of skin
- Specialized connective tissue:
- Adipose tissue
- Reticular tissue
- Cartilage
- Bone
- Muscles: except musculature of iris
- Smooth
- Cardiac
- Skeletal
- All serous membranes
- Blood, lymph, cardiovascular organs
- Substance of cornea, sclera, choroid, ciliary body and iris
- Adrenal cortex
- Gonads and internal reproductive organs
- Spleen
- Kidney and ureter
- Trigone of bladder
- Duramater
Mesodermal Derivative Mnemonic: GONADS
- Genitourinary and Renal
- Others – Muscle, bone, connective tissue, serous lining of body cavities, cardiovascular system, parenchyma
- Notochord – Nucleus pulposus
- Adrenal cortex
- Duramater
- Spleen
Derivatives of Endoderm
Epithelial lining of:
- Respiratory: Larynx, Trachea, Bronchi and Lungs
- Tonsils, Pharynx and GI tract
- Thymus
- Urinary:
- Urinary bladder (except trigone)
- Female urethra (except part of posterior wall)
- Male urethra (except posterior part of prostatic urethra and glandular part)
- Biliary system
- Lower 2/3rd of vagina and Inner surface of labia minora
- Ear:
- Inner layer of tympanic membrane
- Middle ear cavity
- Auditory tube
- Mastoid antrum and air cells
Parenchyma:
- Liver
- Pancreas
- Tonsils
- Thyroid gland
- Parathyroid glands
- Glands of GI tract
- Submandibular gland
- Sublingual gland