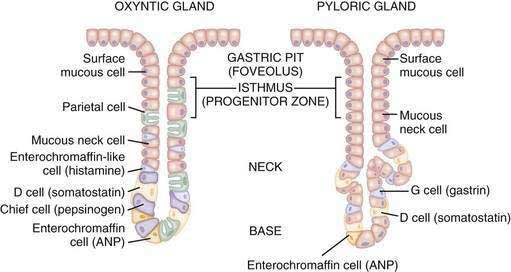
Key player: H+/K+ ATPase or “proton pump” (in canalicular membrane of parietal cells)
a. Hydrogen ions are generated within the parietal cell from dissociation of water. The hydroxyl ions formed in this process rapidly combine with carbon dioxide to form bicarbonate ion, a reaction catalyzed by carbonic anhydrase.
b. Bicarbonate is transported out of the basolateral membrane in exchange for chloride. The outflow of bicarbonate into blood results in a slight elevation of blood pH known as the “alkaline tide“. This process serves to maintain intracellular pH in the parietal cell.
c. Chloride and potassium ions are transported into the lumen of the canaliculus by conductance channels, and such is necessary for secretion of acid.
d. Hydrogen ion is pumped out of the cell, into the lumen, in exchange for potassium through the action of the proton pump; potassium is thus effectively recycled.
e. Accumulation of osmotically active hydrogen ion in the canaliculus generates an osmotic gradient across the membrane that results in outward diffusion of water – the resulting gastric juice is 155 mM HCl and 15 mM KCl with a small amount of NaCl.
A key substrate in the production of gastric acid is CO2, and diffusion of CO2 through the basal surface of the parietal appears to be the rate limiting step in acid synthesis.