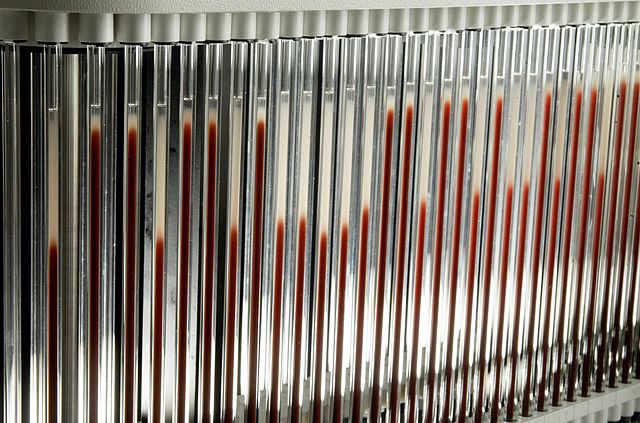
ESR (Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate)
- Usually elevated within 48-72 hours of the infection onset (less reliable in the first 48 hours of infection)
- Continues to rise for 3-5 days after institution of successful therapy and continuing rise beyond 4th-5th day of treatment can be an indication of treatment failure (not good means of monitoring treatment during first week)
- Returns to normal over 2-4 weeks after elimination of infection.
- Elevated in 85%-95% cases of septic arthritis and in 90%-95% of osteomyelitis cases (significantly higher levels in septic arthritis than osteomyelitis)

CRP (C-Reactive Protein)
- Begin to rise within 6 hours of the triggering stimulus (trauma or infection) and then increases several hundredfold
- Reaches a peak within 36-50 hours
- Falls to normal quickly with successful treatment because of short half-life (returns to normal within 1 week of successful treatment)
- Elevated in 98% of patients with osteomyelitis
- If CRP is <1.0 mg/dL, the probability that a patient does not have septic arthritis is 87%
- In the surgery group, it takes twice as long for the CRP and ESR to reach peak values and then twice as long to normalize after initiation of treatment.