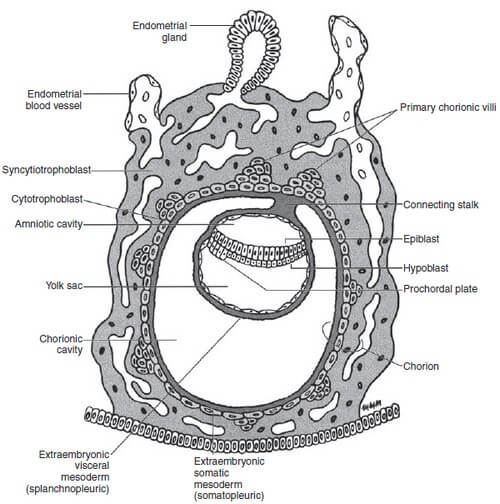
Starting from Day 8, blastocyst progressively invades into the endometrial stroma and there is formation of:
2 layers in Trophoblast:
1. Inner mononulcear Cytotrophoblast (Cellular)
- Mitotic figures are found in the cytotrophoblast – hence generate primary chorionic villi into the syncytiotrophoblast.
2. Outer multinucleated Syncytiotrophoblast (Syncytium – cells have fused)
- Mitotic figures are absent in syncytiotrophoblast – hence, doesn’t divide.
- Day 9: Lacunar stage – vacuoles appear and fuse to form lacunae
- Day 11-12: Establishment of uteroplacental circulation – syncytiotrophoblast penetrate deeper into endometrial stroma and invade the maternal capillaries (sinusoids) and lacunae are continuous with sinusoids
- Implantation site bleeding: Occasionally, bleeding occurs at the implantation site as a result of increased blood flow into the lacunar spaces around 13th day. Because this bleeding occurs near the 28th day of the menstrual cycle, it may be confused with the menstrual bleeding.
- Produce human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
- Stimulates the production of progesterone by the corpus luteum of the ovary (i.e., maintains corpus luteum function). This is clinically significant because progesterone produced by the corpus luteum is essential for the maintenance of pregnancy until week 8. The placenta then takes over progesterone production.
- Can be assessed in blood at day 8 or maternal urine at day 10 for pregnancy testing.
- In early pregnancy, the β-hCG should double every 48 hours; this is used as a benchmark to detect potential ectopic gestation. This is because, syncytiotrophoblast if not implanted into endometrium, would not have enough blood supply to increase the β-hCG twofold in 48 hours.
- hCG is increased in: multiple pregnancy, hydatidiform mole, gestational trophoblastic neoplasia (GTN)
- Hydatidiform mole = Blighted blastocyst (embryo dies) + Hyperplastic proliferation of trophoblast within uterine wall.
2 layers in Embryoblast:
1. Dorsal epiblast (columnar cells)
2. Ventral hypoblast (cuboidal cells)
Together, the epiblast and hypoblast are known as flat bilaminar disc.
2 Cavities:
1. Amniotic cavity (formed from the epiblast cells)
- Epiblast forms amnioblasts that forms the lining of yolk sac adjacent to cytotrophoblast layer.
- Towards hypoblast – epiblast itself lines the amniotic cavity.
2. Yolk sac (formed from hypoblast cells during day 9)
- Hypoblast forms extracoelomic (Heuser’s membrane) that forms the lining of yolk sac adjacent to cytotrophoblast layer.
- Towards epiblast – hypoblast itself lines the yolk sac.
2 cavities + 2 layers of embryoblast = Embryo (Conceptus)
Large cavity surrounding Embryo = Extraembryonic cavity (Chorionic cavity)
Embryo is suspended in the Chorionic cavity by connecting stalk (future umbilical cord)
Between Day 11 and 12: Extraembryonic mesoderm is a new layer of cells derived from the epiblast that lines the extraembryonic (chorionic) cavity.
2 Layers of Extraembryonic mesoderm:
1. Visceral mesoderm (Splanchnopleure): covers the yolk sac
2. Somatic mesoderm (Somatopleure): lines the remaining surface – cytotrophoblast, connecting stalk and amnion