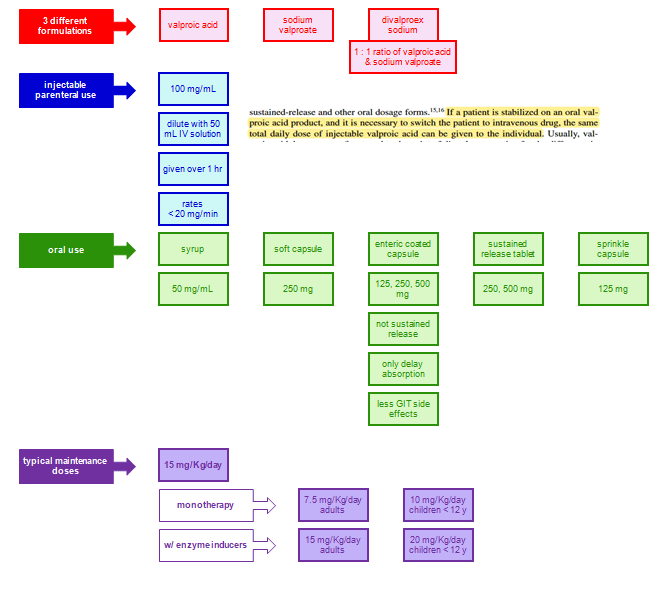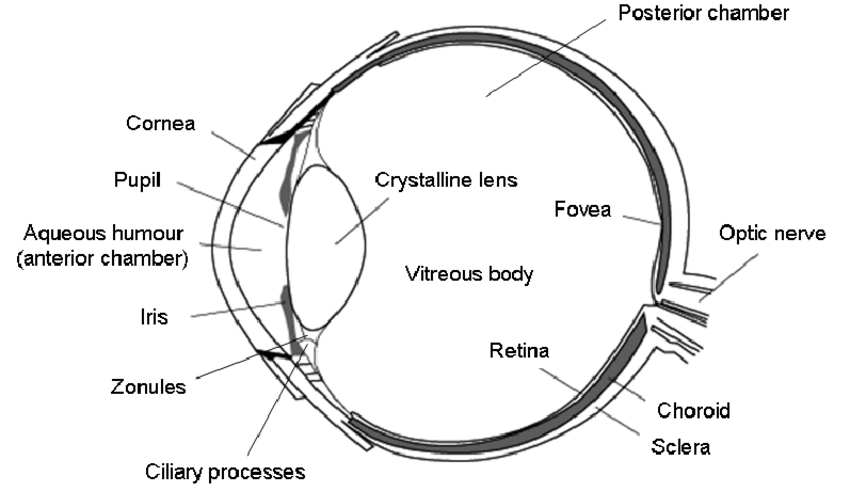
Surface ectoderm derivatives
Mnemonic: LEVeL
- Lens
- Epithelium
- All ocular adnexa including mebomian gland and glands of Zeis and Moll
- Skin
- Cornea
- Conjunctiva
- Vitreous (portion)
- Lacrimal glands and drainage system
Neuro-ectoderm (Optic vesicle and cup) derivatives
Mnemonic: MORE
- Muscles of pupil (constrictor and dilator pupillae)
- Optic nerve
- Retinal pigment epithelium
- Epithelium of iris and ciliary body
Mesoderm derivatives
Mnemonic: MESO
- Muscles (Extraocular)
- Endothelium of eye and orbital blood vessels
- Sclera (temporal portion)
- Others (Vitreous)
All other structures are derived from Neural crest cells.