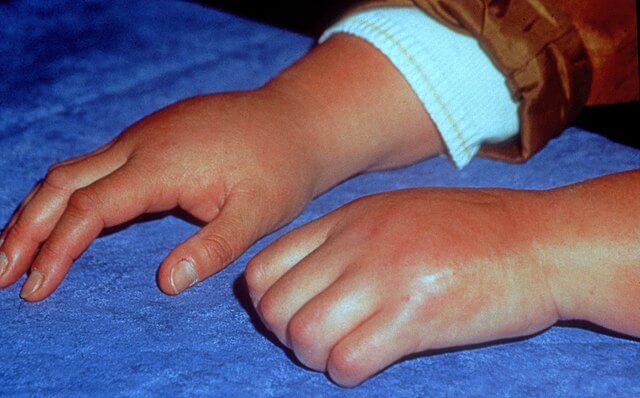
Synonyms: CRPS, Sudeck’s atrophy, Reflex sympathetic dystrophy, RSD, Causalgia
Chronic regional pain syndrome (CRPS) is a persistent neuropathic pain syndrome of an inappropriate intensity due to sustained sympathetic activity with the absence of impending or ongoing tissue damage. There are 2 types of CRPS:
- Type 1 (Sudeck’s atrophy or Reflex sympathetic dystrophy – RSD): no proven nerve injury
- Type 2 (Causalgia): known nerve injury
Budapest Criteria for Clinical Diagnosis
1. Pain (ongoing and disproportionate to any inciting event)
2. Symptoms (reported): At least 1 symptom in 3/4 of the following categories:
- Sensory – Hyperaesthesia and/or allodynia
- Vasomotor – Temperature asymmetry and/or skin color changes and/or skin color asymmetry
- Sudomotor – Edema and/or sweating changes and/or sweating asymmetry
- Motor/Trophic – Decreased range of motion and/or motor dysfunction (weakness, tremor, dystonia) and/or trophic changes (hair, nail, skin)
3. Signs (examined): At least 1 sign in 2/4 of the following categories:
- Sensory – Hyperalgesia (to pinprick) and/or allodynia (to light touch and/or temperature sensation and/or deep somatic pressure and/or joint movement)
- Vasomotor – Temperature asymmetry (> 1 °C) and/or skin color changes and/or asymmetry
- Sudomotor – Edema and/or sweating changes and/or sweating asymmetry
- Motor/trophic – Decreased range of motion and/or motor dysfunction (weakness, tremor, dystonia) and/or trophic changes (hair, nail, skin)
4. Diagnosis of exclusion: No other diagnosis better explains the signs and symptoms.
Mnemonic: CRPS
- Color (Color changes/asymmtery) or Celsius (Temperature asymmetry) – Vasomotor
- Reduced motor function (Reduced ROM/weakness/tremor/dystonia) or keratin health (hair, nail, skin changes) – Motor/trophic
- Pain (ongoing and inappropriate) – Essential criteria
- Swelling or Sweating (changes/asymmetry) – Sudomotor
- Sensory (hyperalgesia/allodynia) – Sensory
Diagnosis requires: 1 Pain + 2/4 Signs + 3/4 Symptoms
Stages of CRPS
| Acute | Dystrophic | Atrophic | |
| Duration | 1-3 months | 3-6 months | Indefinite |
| Pain | Localized, severe & burning | More diffuse, throbbing | Less severe, can involve other extremities |
| Extremity | Warm | Cold, cyanotic, edematous; muscle wasting | Severe muscle atrophy; contractures |
| Skin | Dry and red | Sweaty | Glossy and atrophic |
| X-ray | Normal | Osteoporosis | Severe osteoporosis; ankylosis |
Management of CRPS
Management of CRPS requires a multimodality approach. It can be remembered using the mnemonic:
Mnemonic: 4 P
1. Psychological and cognitive therapy
2. Pharmacological therapy:
- 1st line: Combination of 2 of NSAIDs, TCAs and Anticonvulsants
- 2nd line: Opioids
- 3rd line: Corticosteroids
- 4th line: Lignocaine, Caspaicin or transdermal fentanyl; Calcitonin or bisphosphonates
3. Physiotherapy:
- Active mobilization
- TENS
- Laser therapy
- Ultrasound
4. Pain intervention:
- Spinal cord stimulation
- Peripheral nerve stimulation
- Intrathecal therapy
- Sympathetic blockade
References:
- Goebel A, Bisla J, Carganillo R, et al. A randomised placebo-controlled Phase III multicentre trial: low-dose intravenous immunoglobulin treatment for long-standing complex regional pain syndrome (LIPS trial). Southampton (UK): NIHR Journals Library; 2017 Nov. (Efficacy and Mechanism Evaluation, No. 4.5.) Appendix 3, Research diagnostic criteria (the ‘Budapest Criteria’) for complex regional pain syndrome. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK464482/
- Ping, C.P., & Lam, J.M. (2011). Recommendations on the Management of Neuropathic Cancer Pain.