Osteology
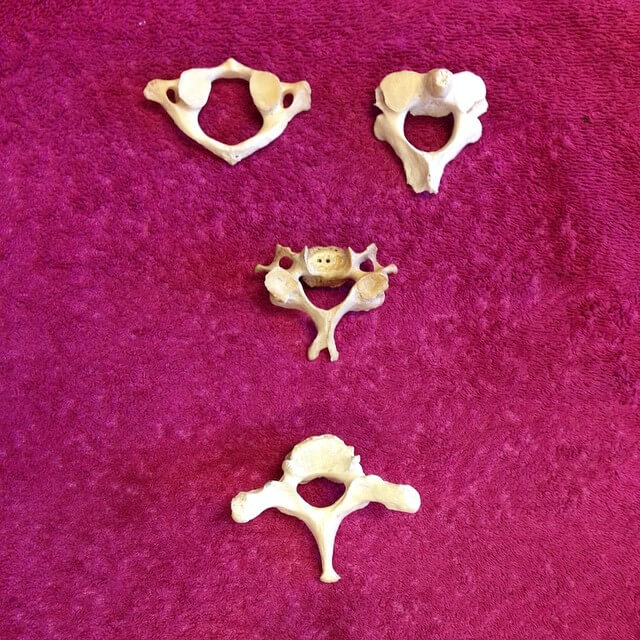
C1 (top left), C2 (top right), Typical vertebra (middle), C7 (down)
| Vertebra | Body | Spinous process | Transverse process |
| Typical (C3-6) | Relatively small; oval; uncinate process superiorly | Bifid | Has foramen transversarium, Has anterior and posterior tubercle separated by groove for spinal nerve (large anterior tubercle in C6 called Carotid/Chassaignac tubercle) |
| Atlas (C1) | None; Ring (2 lateral masses connected by anterior & posterior arches) | None (has posterior tubercle) | Has foramen transversarium; No tubercles |
| Axis (C2) | Has dens (odontoid process) | Bifid | Has foramen transversarium; Has 1 tubercle (posterior) |
| C7 | Larger; uncinate process superiorly | Unifid (longest – vertebra prominens) | Has foramen transversarium (may be small or absent; transmits vein only/doesn’t transmit artery); Has 1 tubercle (posterior) |
Joints or Articulations
| Joint | Articulations | Joint type | Functions |
| Atlanto-occipital (X2) | Superior facets of lateral mass (C1) + Occipital condyles (Cranium base) | Condyloid | “Yes” nodding (flexion-extension) |
| Atlanto-axial (X3) | Lateral = Inferior facets of lateral mass (C1) + Superior facets of C2 Medial = Dens (C2) + Facet for dens (C1) | Lateral (Plane) Medial (Pivot) | “No” movement (rotation) |
| Others | Between vertebral arches (Zygoapophyseal/Facet X 2) = Inferior facets of superior vertebra + Superior facets of inferior vertebra Vertebral bodies (Intervertebral X 1) = 2 vertebral bodies articulated by a “disc” Vertebral bodies (Uncovertebral/Luschka X 2) = Uncinate process of inferior vertebra + Inferolateral aspect of superior vertebra | Zygoapophyseal (synovial) Intervertebral (symphysis/fibrocartilaginous) Uncovertebral (pseudojoints) | Flexion, Extension, Rotation |
Ligaments
- Supraspinous ligament (Liagametum nuchae): Runs between tips of 2 spinous process
- Interspinous ligament: Between 2 spinous processes
- Ligamentum flavum: Connects the laminae of adjacent vertebrae
- Intertransverse ligaments: Run between adjacent transverse processes
- Anterior longitudinal ligament: Between 2 vertebral body (not attached to disc) from sacrum to C2
- C1-C2: Anterior atlantoaxial membrane
- C1-Oc: Anterior atlanto-occipital membrane
- Posterior longitudinal ligament: Between 2 vertebral body (firmly attached to disc) from sacrum to C2
- C2-Foramen magnum: Tectorial membrane
- Apical ligament: Connects apex of dens of C2 to foramen magnum (anterior aspect)
- Alar ligaments: Connects dens of C2 to foramen magnum (lateral aspect)
- Cruciate liagments: Vertical ligaments (Dens to occipital bone and body of C2) + Transverse ligaments (Dens to arch of C1)