APPLICATION: Apply only to a healthy limb or with caution to an unhealthy limb
SIZE OF TOURNIQUET: Arm, 10 cm; leg, 15 cm or wider in large legs
SITE OF APPLICATION: Upper arm; mid/upper thigh ideally
PADDING: At least two layers of orthopaedic felt
SKIN PREPARATION: Occlude to prevent soaking of wool.
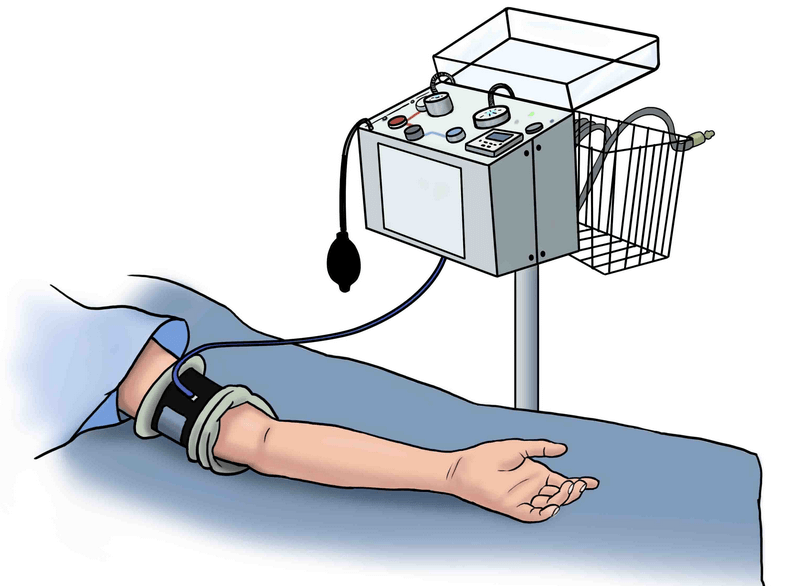
PRESSURE: Use 50-100 mm Hg above systolic for the arm; double systolic for the thigh; or arm 200-250 mm Hg, leg 250-350 mm Hg (large cuffs are recommended for larger limbs instead of increasing pressure)
TIME: Absolute maximum 3 h (recovers in 5-7 days) generally not to exceed 2 h
TEMPERATURE: Avoid heating (e.g., hot lights), cool if feasible, and keep tissues moist
DOCUMENTATION: Duration and pressure
CALIBRATION AND MAINTENANCE: at least weekly calibration and against mercury manometer or test maintenance gauge; maintenance every 3 months
Reference: Modified from Kutty S, McElwain JP: Padding under tourniquets in tourniquet controlled surgery: Bruner’s ten rules revisited, Injury 33:75, 2002.