Synonym: Intercondylar line, Blumensaat’s line
Definition of Blumnesaat line
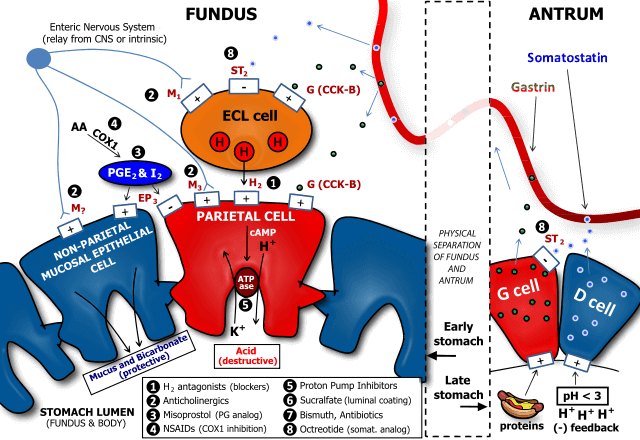
It is the tangent drawn along the roof of intercondylar notch or fossa of the distal femur on the saggital or lateral view.
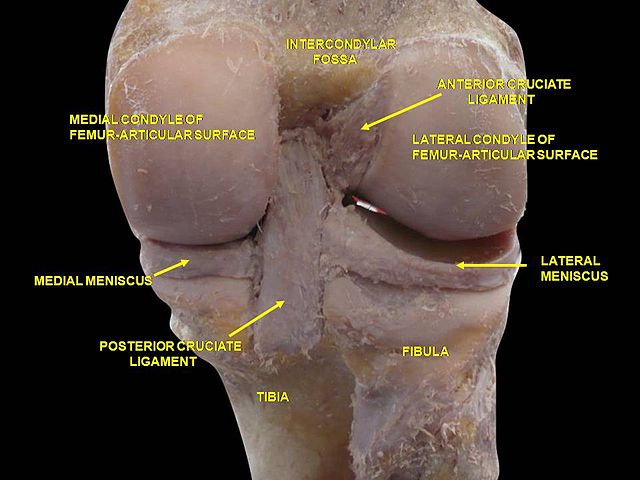
Morphologic variations of Blumensaat line (Iriuchishima’s classification)
Straight type (35%): appear more or less straight
Small hill type (25%): a protrusion spanning less than half of the line was at the posterior (proximal) part of the Blumensaat’s line.
Large hill type (45%): a protrusion spanning more than half of the line was at the proximal part of the Blumensaat’s line
Ludloff’s triangle
The Blumensaat line forms the base of the Ludloff’s triangle, the other sides represented by the patellar surface and the epiphyseal line.
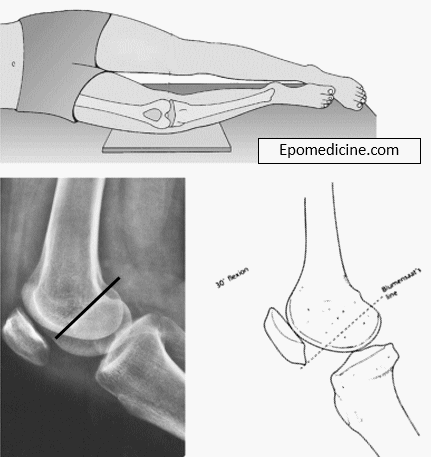
Anatomy of Intercondylar notch
Synonyms: patellar groove, patellar sulcus, patellofemoral groove, femoropatellar groove, femoral groove, femoral sulcus, trochlear groove of femur, trochlear sulcus of femur, trochlear surface of femur, or trochlea of femur.
Clinical uses and importances of Blumensaat line
It provides proximal attachment to Anterior and Posterior cruciate ligaments of knee (ACL and PCL).
1. Retrograde femoral nailing: On the lateral view, the entry point of intramedullary nail must be at the anterior tip of the Blumensaat’s line. Starting posterior may damage the cruciate ligaments when reaming.
2. Distal femoral fracture fixation: The plate should lie anterior and proximal to the Blumensaat’s line. When placing the most distal and posterior screw in the condylar segment, if the hole is posterior to the Blumensaat’s line, a short screw should be placed to avoid violation of intercondylar notch.
3. Location of lateral femoral condyle sulcus: This can be visualized as a shallow indentation in the convex contour of the condyle in the lateral view. Sulcus terminalis of the lateral femoral condyle is more distinct as compared to that of the medial condyle. A normal sulcus is located within 10 mm of the Blumensatt’s line in lateral view. A notch depth of 1.5 mm is a useful sign in torn ACL.
4. Relative position of patella: In a 30 degree flexed knee, the Blumensaat’s line should intersect the lower pole of patella. It may indicate patella baja (low lying) or alta (high riding).
5. ACL-Blumensaat line angle: It is the angle between the intersection of the Blumensaat line and a line parallel to the distal portion of ACL. An angle of >15º indicates an abnormal course and probable ACL tear.
6. ACL reconstruction: The inferior portion of the femoral component of the graft must be at the intersection of the Blumensaat’s line and a line drawn along the posterior cortex of the femur. Tibial component of the graft should be entirely posterior to and parallel or more steep to the Blumensaat line.
References:
1. Iriuchishima, T., Goto, B., Ryu, K., & Fu, F. H. (2019). The Blumensaat’s line morphology influences to the femoral tunnel position in anatomical ACL reconstruction. Knee Surgery, Sports Traumatology, Arthroscopy. doi:10.1007/s00167-019-05492-5
2. Radiopedia.org, the wiki-based collaborative Radiology resource