The objectives of intravesical therapy in bladder cancer is to:
- avoid post-TURB (Transurethral resection of bladder) implantation of tumor cells
- eradicate residual disease
- prevent tumor recurrence
- delay or reduce tumor progression
Indications of BCG in bladder cancer:
- Intravesical treatment and prophylaxis of bladder CIS
- Prophylaxis of primary or recurrent stage Ta and/or T1 papillary tumors following TUR
It is not recommended for Ta low-grade papillary tumors, unless they are judged to be at high risk of recurrence.
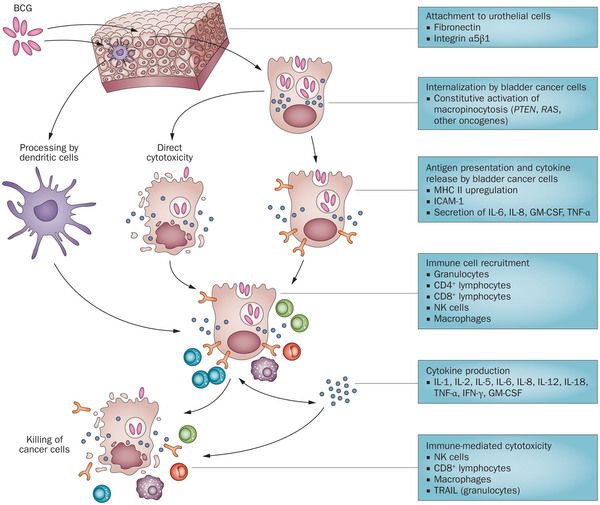
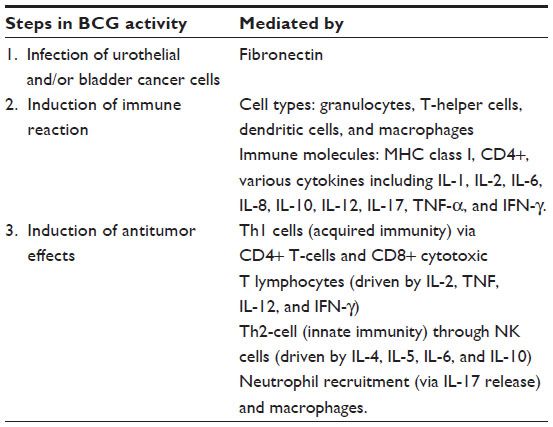
Mechanism of action of BCG in bladder cancer:
Pre-requisites of Intravesical BCG:
Urine R/E and Urine cultures: Defer treatment until clearance if –
- Leukocytes: 100 X 10^6/L
- Bacterial growth or specific organism identified
- Macroscopic hematuria
With UTI, BCG can cause BCG cystitis and the antibiotics administered for UTI can decrease the BCG efficacy as BCG bacilli are sensitive to wide range of antibiotics.
Dispensary: Powder 81 mg (TheraCys), 50 mg (Tice BCG) – both reconstituted to 50 mL volume
Procedure:
- Under all aseptic conditions bladder is catheterized and urine is drained
- 50 ml suspension of intravesical BCG is instilled
- Following instillation, patient should lie prone for 15 minutes
- Then patient is allowed to move freely to ensure the drug has the opportunity to bathe all parts of the bladder mucosa. The drug needs to remain in the patient’s bladder for at least 1 hour (to a maximum of 2 hours).
- At the end of 2 hours, have the patient void in a seated position for safety reasons.
- Instruct the patient to increase fluid intake in order to flush the bladder in the hours following BCG treatment.
Note: Do not administer less than 2 wk after resection; do not administer intravesical forms SQ or IM. If TheraCys is administered within two weeks of either biopsy, TUR or traumatic bladder catheterization (associated with hematuria), a systemic BCG reaction is much more likely to occur.
Regimen:
1 vial prepared & instilled in bladder for 2 hr.
- Induction: Repeat once/wk × 6 weeks
- Maintenance: At 3, 6, 12, 18, & 24 months
Contraindications:
- Known hypersensitivity
- Immunosuppresion: risk of disseminated BCG infection
- History of systemic BCG reaction
- Concurrent febrile illness, UTI or macroscopic hematuria
- Active tuberculosis
Side effects:
- Hematuria
- Urinary frequency
- Dysuria
- Bacterial UTI
- BCG sepsis
- Malaise
- Fever, chills, pain, nausea/vomiting, anorexia
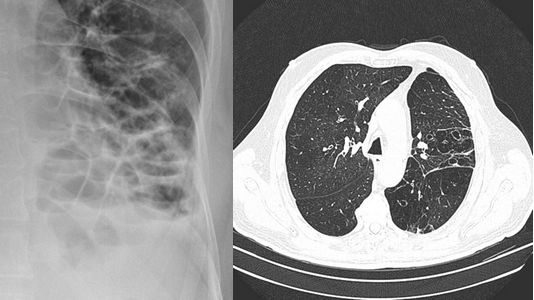
BCG sepsis:
BCG sepsis: Potentially life-threatening event secondary to intravasation of intravesical BCG resulting in cardiovascular collapse and acute respiratory distress
- Possible etiologies include hypersensitivity reaction and bacterial sepsis
“BCG-osis” is a term used to refer to disseminated disease in patients treated with BCG
- The lungs and liver are typically involved
- Patients are usually hemodynamically stable
“Systemic BCG reaction” may be defined as the presence of any of the following signs, if no other etiologies for such signs are detectable: fever >39.5°C for > or = 12 hours; fever >38.5°C for > or = 48 hours; pneumonitis; hepatitis; other organ dysfunction outside of the genitourinary tract with granulomatous inflammation on biopsy; or the classical signs of sepsis, including circulatory collapse, acute respiratory distress, and disseminated intravascular coagulation.
Risk factors:
- Inadequate delay after transurethral instrumentation (TURBT or bladder biopsy)
- Traumatic catheterization or gross hematuria at time of intravesical instillation
Treatment:
- If antitubercular therapy required, intravesical BCG should be discontinued
- Mild/moderate symptoms including low-grade fevers <48 hr (BCG cystitis):
- Analgesics
- NSAIDs
- +/– Fluoroquinolone: levofloxacin 500 mg/d
- Antitubercular medications should be initiated for signs of sepsis or severe cystitis symptoms >48 hr
- Typically isoniazid 300 mg/d and rifampin 600 mg/d for 3–6 mo
- For solid organ involvement, ethambutol 15 mg/kg/d added
- BCG resistant to cycloserine and pyrazinamide
- Prednisone 40 mg/d recommended for septic shock or if hypersensitivity reaction suspected
References:
- 5 minutes Urology consult
- Intravesical Chemotherapy and BCG for the Treatment of Bladder Cancer: Evidence and Opinion (European Association of Urology)