Synonyms: Radial fossa, Foveola radialis
Note: Depression in the humerus which receives the head of radius is also named as Radial fossa
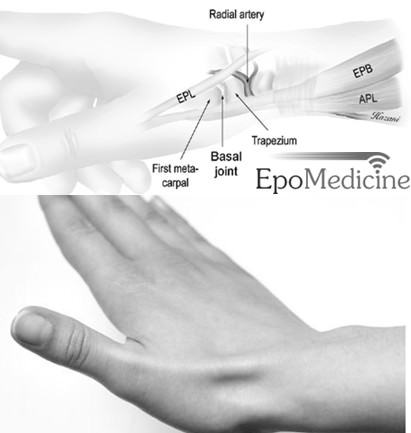
Definition: It is a triangular shaped depression in the radial or lateral aspect of the dorsum of the hand which is seen when the thumb is extended fully. This hollow was used to snuff powdered tobacco and hence named as Anatomical snuff box.
Boundaries and Borders:
- Medial border: Extensor Pollicis Longus (EPL)
- Lateral border: Extensor Pollicis Brevis (EPB) and Abductor Pollicis Longus (APL)
- Proximal border: Styloid process of radius
- Distal border: Base of 1st metacarpal
- Floor: Scaphoid and Trapezium bones
- Roof: Skin
Contents:
- Radial artery
- Radial nerve: Dorsal cutaneous branch of radial nerve
- Cephalic vein
Note: Some books regard scaphoid and trapezium as contents of the snuff box.
Clinical Applications:
1. Differential diagnosis of Anatomical snuff box pain or tenderness:
- DeQuervain’s tenosynovitis: Inflammation of the 1st extensor compartment of the wrist i.e. EPB and APL
- Scaphoid fracture
- Fracture of 1st metacarpal or distal radius
- Scapholunate dislocation
- Extensor carpi radialis or Flexor carpi radialis strain
- Arthritis of Carpo-metacarpal or Radio-carpal joint
- Cheiralgia paresthetica (handcuff neuropathy): compression or trauma of superficial branch of radial nerve
- C6 cervical radiculopathy
2. Finkelstein’s maneuver (for DeQuervain’s tenosynovitis): Making a fist over thumb and ulnar deviation of wrist stretches the tendons of 1st extensor compartment causing significant pain.
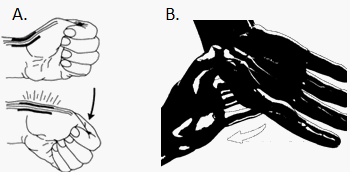
B. Scaphoid shift or Watson test
3. Signs of Scaphoid fracture:
- Anatomical snuff box tenderness on palpation
- Scaphoid tubercle tenderness (Location: extensor carpi radialis at palmar crease)
- Scaphoid compression test (thumb is compressed against scaphoid)
4. Scaphoid shift or Watson test (Press scaphoid tubercle with thumb while moving wrist from ulnar to radial deviation): Pain or clunk suggests scapho-lunate instability
5. Why scaphoid is vulnerable to avascular necrosis?
- 80% scaphoid surface is cartilage, leaving a small area for arterial blood supply to enter the bone.
- Major blood supply is from dorsal carpal branch of radial artery which runs distal to proximal.