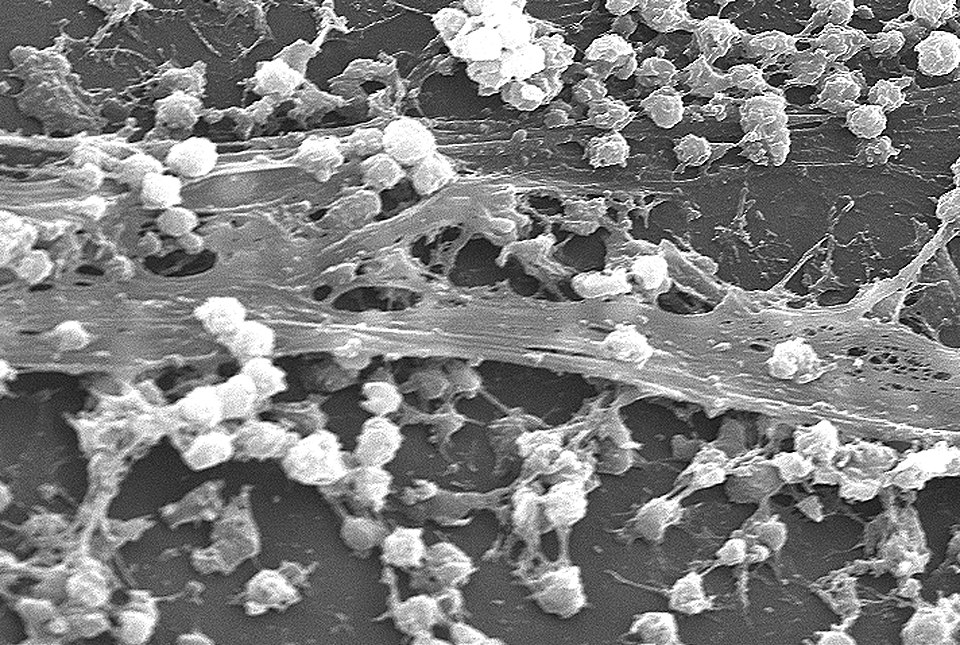
Biofilms are immobile microbial communities which colonize and grow on surfaces of medical implants such as sutures, catheters and implants, by self-produced extracellular polymeric substances and cause infections which can only be treated by their removal. It provides additional resistance to the bacteria by various mechanisms like altered pH, osmolarity, nutrients scarcity, mechanical and shear forces and blocking the access of bacterial biofilm communities from antibiotics and host’s immune cells.
Antibiotics active against both gram positive and negative:
1. Fluoroquinolones:
- Many guidelines recommend FQs as a first-line option for targeting biofilm by gram-negative microorganisms and for combination therapy with rifampicin for gram-positive pathogens, including MRSA.
2. Fosfomycin
3. Tetracyclines
Antibiotics active against gram-positive:
1. Rifampicin or Rifampin
2. Fusidic acid
3. Glycopeptides (Vancomycin and Teicoplanin)
4. Lipopeptides (Daptomycin)
5. Lipoglycopeptides (Oritavancin, Dalbavancin, Telavancin)
Antibiotics active against gram-negative:
1. Colistin
According to the author of the article 1, their preferred treatment of choice for gram-positive PJIs includes a short course of IV beta-lactams followed by oral step-down therapy combining an antibiofilm agent, preferably rifampicin. In the case of gram-negative PJIs they preferred the Fluoroquinolones, particularly ciprofloxacin. Whenever possible, the combination of rifampicin and fluoroquinolones for the definitive treatment of gram-positive PJIs was favored.