Periphery of physis:
The physis is connected to the epiphysis and metaphysis peripherally via:
- Groove of Ranvier (supplies chondrocytes to the periphery for latitudinal or appositional growth)
- Perichondral ring of LaCroix (strong fibrous tissue that anchors physis to metaphysis)
Blood supply of physis:
There are three sources of blood supply to the physis: the epiphyseal, metaphyseal, and perichondral circulations.
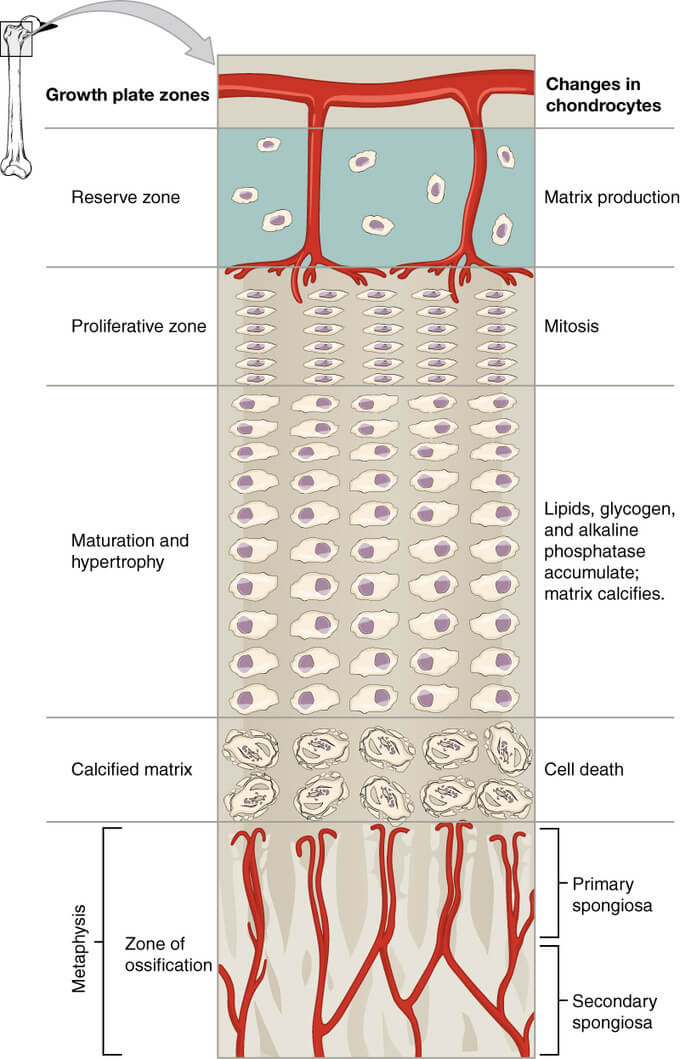
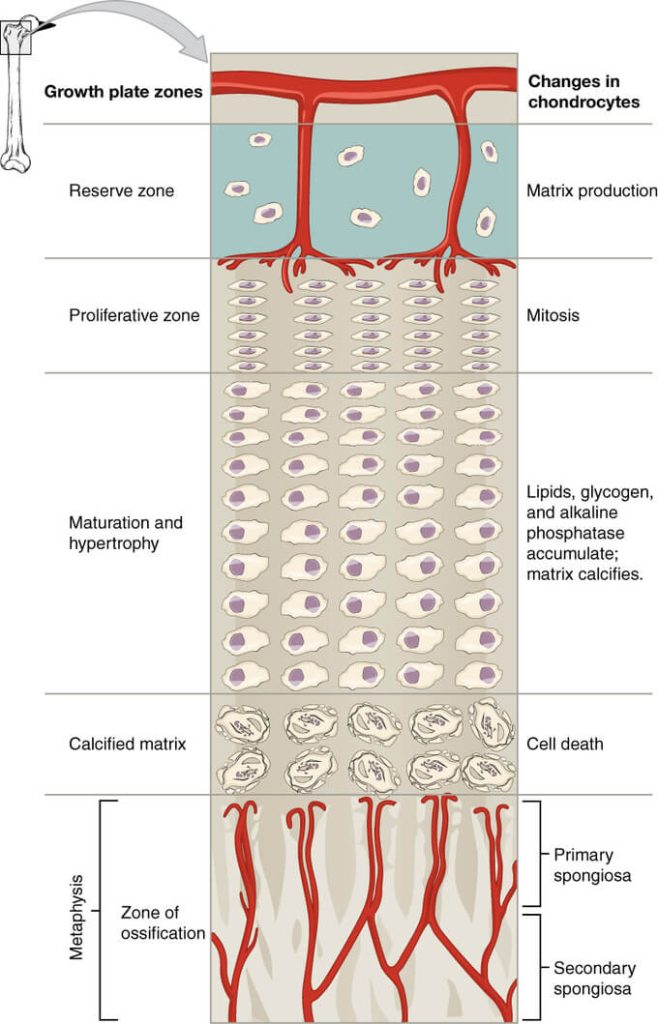
Zones of physis:
| Zones | Characteristics | Functions | Blood supply | Diseases |
| Epiphysis | Epiphyseal artery | Multiple Epiphyseal Dysplasia (MED) | ||
| Physis | ||||
| 1. Reserve (Resting) zone | Germinal cells of stem cell origin (responsive to hormones) surrounded by mechanically strong thick layer of matrix | Matrix production Storage | Epiphyseal arteries descend through the layer but do not supply (low oxygen tension) | 1. Diastrophic dysplasia 2. Pseudo-achondroplasia 3. Gaucher’s disease |
| 2. Proliferative (Columnar) zone | Stacking of chondrocytes longitudinally; surrounded by mechanically strong thick layer of matrix | Matrix production Cellular proliferation | Excellent (excellent oxygen tension) | 1. Achondroplasia 2. Hypo-achondroplasia 3. Gigantism |
| 3. Hypertrophic zone | Hypertrophy of chondrocytes (5-10 times) with less space for matrix (weakest layer) | SCFE (non-renal failure) Enchondroma | ||
| a. Maturation zone | Preparation of matrix for calcification | Low (low oxygen tension) | Mucopolysaccharidosis | |
| b. Degenerative zone | Preparation of matrix for calcification | Lower (lower oxygen tension) | Mucopolysaccharidosis | |
| c. Zone of provisional calcification | Programmed cell death of chondrocytes | Calcification of matrix | Nil (poor oxygen tension) | 1. Rickets & Osteomalacia 2. Physeal fractures |
| Metaphysis | Metaphyseal & nutrient artery branches | |||
| 1. Primary spongiosa | Bone formation | Good (good oxygen tension) | 1. Metaphyseal chondrodysplasia 2. Acute hematogenous osteomyelitis 3. Corner fractures 4. SCFE (renal failure) | |
| 2. Secondary spongiosa | Remodeling | Excellent (excellent oxygen tension) | 1. Osteopetrosis 2. Osteogenesis imperfecta 3. Scurvy 4. Metaphyseal dysplasia |
The hypertrophic zone is therefore the weakest layer of the physis under tension, shear, and bending stress, and it is the most common area for fractures.