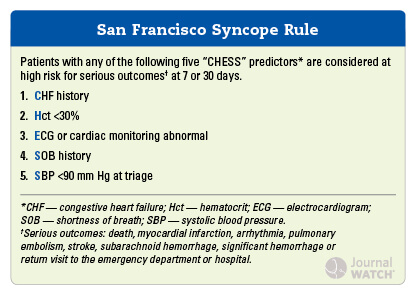
San Francisco Syncope Rule (SFSR) defines high risk criteria for patients with syncope.
FED 30 90
- Failure (Congestive heart failure)
- ECG abnormalities
- Dyspnea (shortness of breath)
- Hematocrit <30%
- Systolic blood pressure <90 mmHg (at any time)
Presence of any of the above criteria is regarded as positive.
Mnemonic: CHESS
- Congestive heart failure
- Hematocrit <30%
- ECG abnormality
- Shortness of breath
- Systolic blood pressure <90 mmHg
This rule has a 96% sensitivity and 62% specificity for serious outcome – negative predictive value: 99.2%; positive predictive value 24.8%. However, an external validation at the Albert Einstein College of Medicine showed a lower sensitivity of 74%.
Serious outcome in this study is defined as “death, myocardial infarction, arrhythmia, pulmonary embolism, stroke, subarachnoid hemorrhage, significant hemorrhage, or any condition causing a return ED visit and hospitalization for a related event.”