Gustilo Anderson Classification
Mnemonics:
1. Parameters: ABCD’S (Area, Bone, Circulation, Dirt, Soft tissue)
2. Classification: I, II, III then A, B, C
Progression for grade I to III C implies a higher degree of energy involved in the injury, higher soft tissue and bone damage, and higher potential for complications.
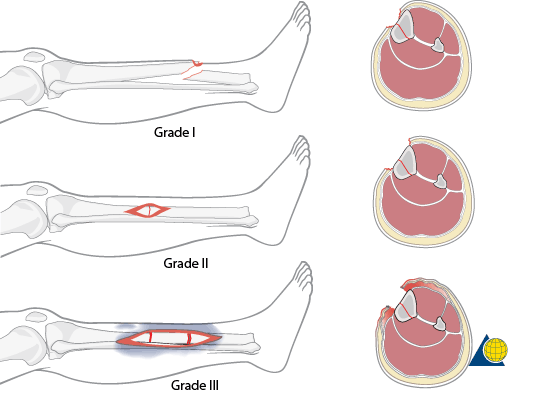
Type I: 1 cm or smaller wound, Grade I injury (minimal energy trauma, soft tissue damage, contamination or comminution)
Type II: 2 cm or larger wound, Grade II injury (moderate energy trauma, soft tissue injury, contamination or communition)
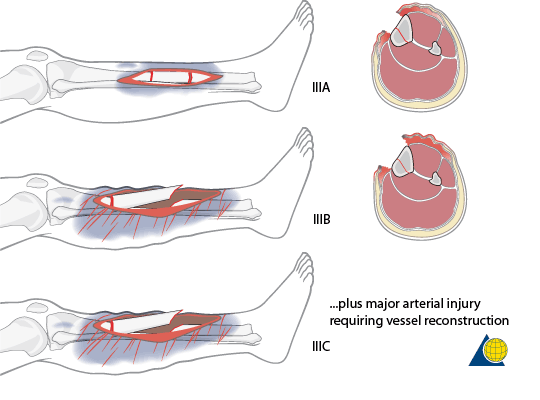
Type III: >10 cm; Severe/extensive energy trauma, soft tissue injury, contamination or communition or segmental fractures
- III A: Adequate soft tissue coverage of bone
- III B: Bony exposure
- III C: Compromise of neurovascular status
These are automatically Type III open fractures:
- Fractures >8 hours old
- Farmyard injuries
- Gunshot injuries
- Traumatic amputation
Infection rate:
Class I: 0-2%
Class II: 2-5%
Class IIIA: 5-10%
Class IIIB: 10-50%
Class IIIC: 25-50%
Swanson, Szabo and Anderson Classification for Open fractures of Hand
Mnemonic: ABCD’S
1. Animal bite
2. Barnyard injury
3. Comorbidities (Diabetes, hypertension, rheumatoid arthritis, hepatitis, asthma, etc.)
4. Dirt/Debris
5. Delay in treatment of 1 Day (>24 hours)
6. Stream (warm lake/river) injury
All of the above are absent: Type I (infection rate – 1.4%; primary closure suitable)
Any of the above present: Type II (infection rate – 14%; delayed closure suitable)
Mangled Extremity Severity Score (MESS) to Predict Eventual Amputation
Mnemonic: MESS
1. Maturity (Age):
- <30 years: 0
- 30-50 years: 1
- >50 years: 2
2. Extremity ischemia:
- Pulse reduced or absent but perfusion normal: 1
- Pulseless (by doppler), paresthesia, diminished capillary refilling, diminished motor activity: 2
- Pulseless, cool, paralysed, insensate, numb, without capillary refill: 3
3. Skeletal and soft tissue injury:
- Low energy (stab; simple fracture; pistol gunshot): 1
- Medium energy (open or multiple fractures; dislocations): 2
- High energy (high speed MVA; rifle gunshot; close shotgun): 3
- Very high energy (crush): 4
4. Shock:
- Normotensive (SBP >90 mmHg): 0
- Transient hypotension (resposnive to fluid): 1
- Persistent hypotension (non-responsive): 2
Interpretation:
- Score is doubled for ischemia >6 hours.
- MESS >7 predicts eventual amputation.
For Open fractures type IIIA and IIIB, Ganga Hospital Open Injury Severity Score (GHOISS) has similar sensitivity but higher specificity than MESS and hence, is a much better predictor of amputation. A score >14 is an indicator for amputation.
Rule of 3 for Open fractures
Antibiotics
3 possible antibiotics:
- 1st generation cephalosporin +/-
- Aminoglycoside (for grade III) +/-
- Metronidazole (for possible anaerobic contamination)
According to BOA and BAPRAS:
- Initial prophylaxis: Co-amoxiclav, Cefuroxime or Clindamycin (in penicillin allergic)
- At Debridement: Add stat Gentamicin to above
- At skeletal stabilization and definite wound cover: Gentamicin and Vancomycin or Teicoplanin must be given on time on induction of anesthesia (vancomycin should be started atleast 90 minutes prior to surgery)
Initiate antibiotics as early as possible (within 3 hours)
Continue initial prophylaxis until soft-tissue closure or maximum of 3 days whichever is shorter.
Irrigation fluid volume
Gustilo-Anderson Class I = 1 X 3 L = 3 L
Gustilo-Anderson Class II = 2 X 3 L = 6 L
Gustilo-Anderson Class III = 3 X 3 L = 9 L
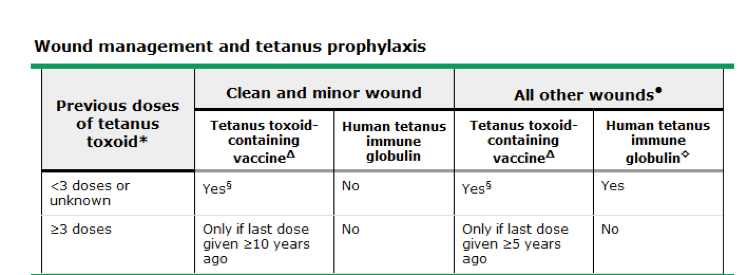
Tetanus Prophylaxis
Mnemonic:
Less than three, give TT
And wound is bad, give antibody
If it’s at least three, think of last dose
1. You don’t need to think of HTIG if the wound is clean or if the patient has received 3 or more doses of TT.
2. If <3 doses of TT – TT needs to be given
3. If 3 or more doses of TT – HTIG is not needed; TT is needed if last dose as taken 5-10 years ago in dirty wound and more than 10 years ago in clean wound.