Hematoma block is a technique in which a local anesthetic agent is injected directly into the hematoma surrounding the fracture, the location of which is confirmed by aspirating blood into the syringe.
Indications of Hematoma Block
- Commonly used for distal radius fractures, metacarpal fractures, tibial shaft fractures, and ankle fractures
- Any diaphyseal or metaphyseal fracture is amenable to a hematoma block
Contraindications of Hematoma Block
- Allergy to local anesthetics
- Overlying infected or dirty skin
Hematoma blocks typically are ineffective in open fractures.
Mechanism of action of Hematoma Block
The fracture hematoma acts as a fluid medium – injection of anesthetics into the hematoma results in diffusion of the anesthetic around the fracture site.
The anesthetic inhibits the generation and conduction of painful impulses primarily in small nonmyelinated nerve fibers in the periosteum and local tissues.
Local Anesthetic for Hematoma Block
2% Lidocaine without epinephrine or 0.5% Bupivacaine
- Preferably mixture of 5 ml lidocaine and 5 ml bupivacaine (for adult)
- Or age-appropriate lower dose
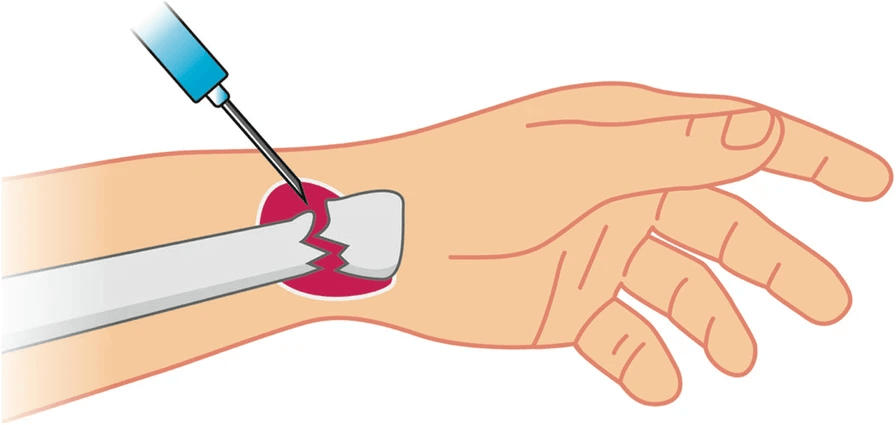
Landmarks for Hematoma Block
- Soft tissue landmark pre-determined from radiograph
- Palpable step-off deformity
Technique of Hematoma Block
- Antiseptic precautions
- Using 22-25 G needle and 10 ml syringe, enter the skin directly over fracture
- Aspirate the needle while advancing it to avoid intravascular placement of anesthetic (return of very dark blood suggests that the hematoma has been reached)
- Inject 5-10 ml anesthetic using barbotage technique while being vigilant for any warning signs of intravascular injection
- Inject another 5 ml into the surrounding periosteum
- Remove the needle and apply sterile bandage
- Wait for 10-15 minutes before attempting reduction of fracture
Complications of Hematoma Block
- Conversion of closed fracture to open fracture (only theoretical risk)
- Compartment syndrome
- Temporary paralysis of anterior interosseous nerve (AIN)
- Acute carpal tunnel syndrome
References:
- Handbook of Splinting and Casting By Stephen R. Thompson, Dan A. Zlotolow (2011)
- Rockwood and Wilkins’ Fractures in Children Volume 3 By Charles A. Rockwood (2010)