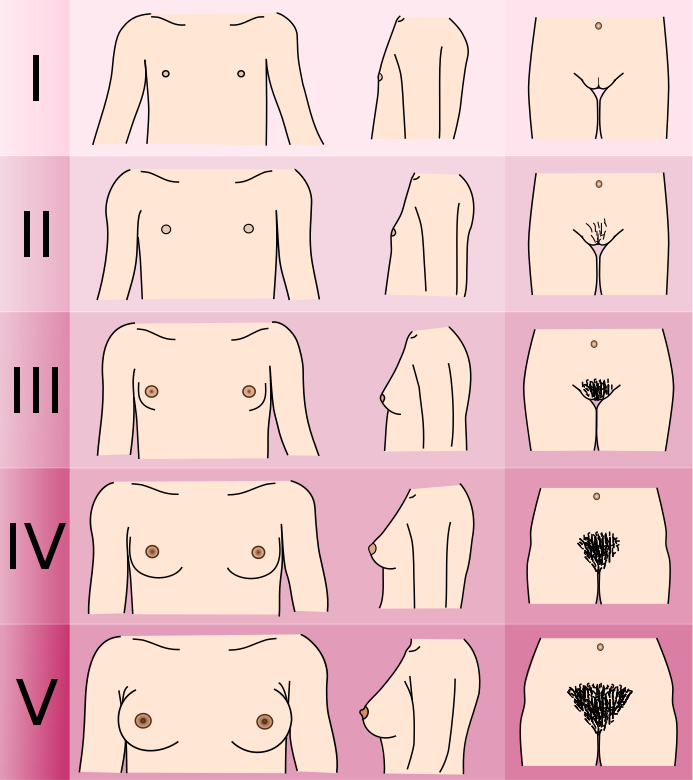
Breast Development
Mnemonic: ABCDE
- Stage 1 – Absent development
- Stage 2 – Breast bud
- Stage 3 – Common Contour (not separated)
- Stage 4 – Double mound (contour separated)
- Stage 5 – End stage development (Adult type)
Male Genitalia Development
Mnemonic: ABCDE
- Stage 1 – Absent development
- Stage 2 – Bulky testes and scrotum
- Stage 3 – Cock lengthens
- Stage 4 – Darkening of scrotum
- Stage 5 – End stage development (Adult type)
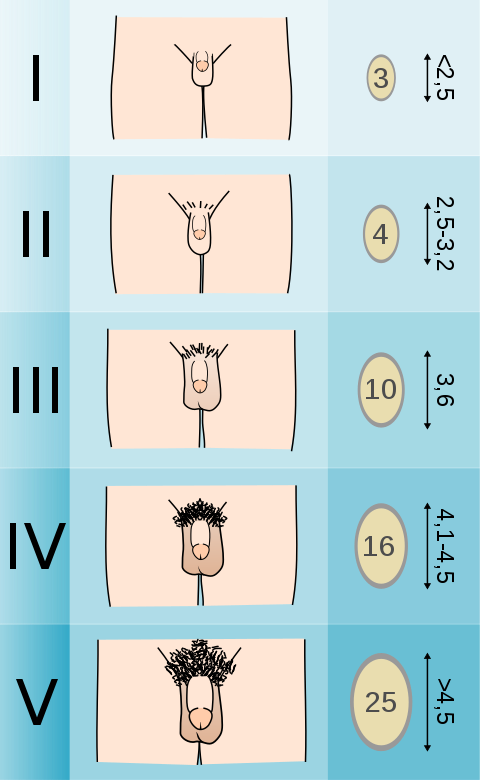
Pubic Hair Development
Mnemonic: A Small CAT
- Stage 1 – Absent
- Stage 2 – Straight
- Stage 3 – Curling
- Stage 4 – Adult
- Stage 5 – Thighs
| Female | Both | Male | |
| Stage | Breast | Pubic Hair | Genitalia |
| 1 | Preadolescent | None | Childhood size |
| 2 | Breast bud | Sparse, straight | Enlargement of scrotum, testes |
| 3 | Areolar diameter enlarges | Darker, curling | Penis grows in length; testes continue to enlarge |
| 4 | Secondary mound; separation of contours | Coarse, curly, adult type | Penis grow in length/breadth; scrotum darkens, testes enlarge |
| 5 | Mature female | Adult, extends to thigh | Adult shape/size |
Excellent