Check S4-5
S4-5: Perianal area <1 cm lateral to the mucocutaneous junction (taken as one level)
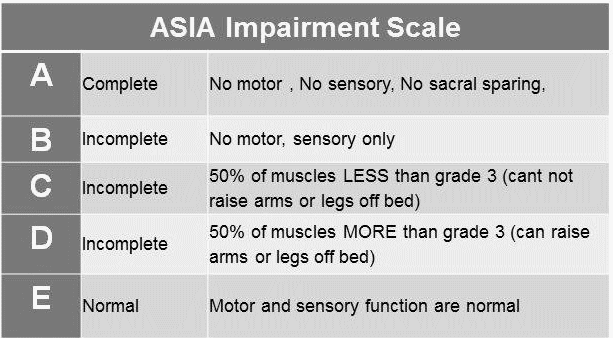
1. Sensory (-) and Motor (-): AIS A (Complete)
i.e. N-0-0-0-0-N sign (No sacral sparing)

2. Sensory (+) and Motor (-): AIS B
i.e. Sensory (+) means any sensation present in S4/S5 or anal sensation
Motor (-) means no Voluntary Anal Contraction
3. Sensory (+) and Motor (+): AIS C or D
Check Motor Function
- Motor 0/5, >3 levels below motor level: AIS B
- Motor 1/5 or 2/5 in atleast 1/2 of key muscles below NLI (Neurologic Level of Injury): AIS C
- Motor 3/5 or more in atleast 1/2 of key muscles below NLI: AIS D
Sensory and Motor Normal in All Segments
- Prior deficits: AIS E
- No prior deficits: Cannot be graded
Important Points
1. Sensory level: Lowest dermatome with both sensation 2/2 and all segments above being 2/2.
2. Motor level: Lowest myotome with motor 3/5 or more with all myotome above being 5/5.
3. Sensory level where motor level cannot be tested (C2-4, T2-L1, S3-5): Motor level is considered the same as sensory level.
4. Neurologic Level of Injury (NLI): Sensory and motor level may be different for right and left producing 4 possible levels (right sensory, left sensory, right motor, left motor). NLI is the highest level among these 4.
5. Zone of Partial Preservation (ZPP) irrespective of AIS grade: Lowest dermatome or myotome on each side with some preservation. Previously it was assessed only for AIS A. Prognosis of the lower extremity motor score after one year is more reliable with the new definition of the ZPP.
- Motor ZPP: can be assessed in all cases with absent VAC
- Sensory ZPP: can be assessed in side of absence of S4-S5 sensation (LT,PP) and absent DAP
6. Motor score: 10 key muscle groups tested in SUPINE position and scored 0 to 5 or NT (not tested).
- Max. score for each limb = 5 X 5 = 25 (Maximum = 25 X 4 = 100)
7. Sensory score: 28 dermatomes tested for Light touch/LT (posterior column – use cotton tip applicator) and Pin Prick/PP (spinothalamic tract – use safety pin) and scored 0 to 2 or NT (not tested).
- Max. score for PP or LT on each side = 2 X 28 = 56 (Maximum = 56 X 4 = 224)
8. When to test non-key muscles?
In a patient with an apparent AIS B classification, non-key muscle functions
more than 3 levels below the motor level on each side should be tested to
most accurately classify the injury (differentiate between AIS B and C).
9. ‘*’ – concept:
- Abnormal examination scores can be tagged with a ‘*’ to indicate that a non-SCI condition impacts the examination results
- Can be applied for scores except M5 and S2
- All grades affected by ‘*’ should also have ‘*’
- Approach: Classify, Reclassify and Add ‘*’ to the differing variables
Further reading of cases and examples of ASIA grading:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3232636/
https://www.med.unc.edu/phyrehab/files/2017/12/asia-presentation.pdf
ASIA 2019 revision
ASIA-ISCOS 2019 Worksheet