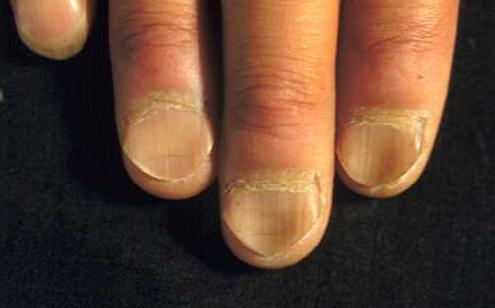
Synonyms: Spoon-shaped nails, Concave nails
Definition of koilonychia: Loss of longitudinal and lateral convexity of the nail, with thinning and fraying of the distal portions.
Conditions associated with koilonychia:
- Normal variant
- Soft nails with occupational damage
- Iron deficiency anemia
- Hemochromatosis
- Raynaud’s syndrome
- Psoriasis (Koilonychia with subungual keratosis)
Mechanism of koilonychia in Iron Deficiency Anemia:
Koilonychia occurs in 5.4% of the patients with iron deficiency. It is thought to occur due to the upward deformation of lateral and distal portions of pliable iron deficient nail plates under mechanical pressure. Nail matrix changes due to blood flow abnormalities was also proposed as a pathomechanism. It is reversible with replenishment of iron stores.
Clinical test to detect koilonychia:
In mild cases, the water test may enable a drop of water to be retained on the nail plate.
References:
- M Razmi T, R V Nampoothiri, S Dogra; Koilonychia in iron deficiency, QJM: An International Journal of Medicine, Volume 111, Issue 4, 1 April 2018, Pages 271–272
- A Text Atlas of Nail Disorders: Techniques in Investigation and Diagnosis edited by Robert Baran, Ivan Bristow, Rodney P. R. Dawber, Ekart Haneke, Antonella Tosti


Yes my name is Larry and I have this and my nails are also a brownish color and really would like help for it what can I do