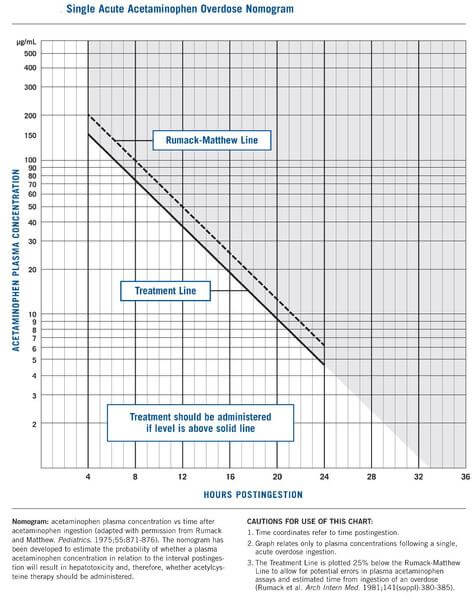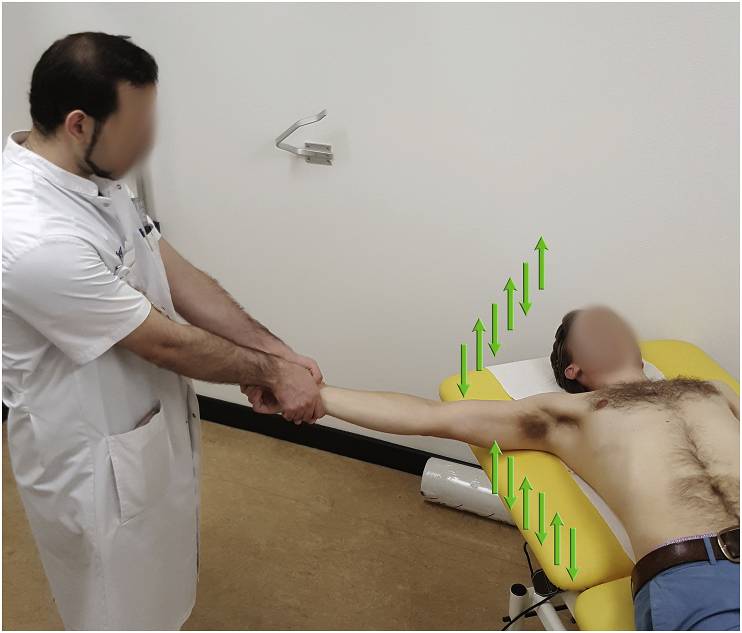
Indication: Anterior shoulder dislocation
Position of patient: Supine
Position of physician: Standing on the side of the dislocated shoulder
Steps:
- Physician holds the wrist of the patient with both the arms keeping elbow of the patient extended and forearm in neutral position
- Arm is slowly abducted in brief oscillating movement (about 5 cm up and down movement – 2 to 3 oscillations per second)
- After 90 degrees of abduction, add external rotation while continuing oscillations
- Reduction is usually achieved around 120 degrees of abduction
- After achieving reduction, slowly internally rotate the arm to bring the forearm to lie across the patient’s chest
Success rate: 88-95%
Reduction time: 2-3 minutes
Pain: 1-2 out of 10 on VAS scale
Reference: Alkaduhimi H, van der Linde JA, Flipsen M, van Deurzen DF, van den Bekerom MP. A systematic and technical guide on how to reduce a shoulder dislocation. Turk J Emerg Med. 2016 Nov 18;16(4):155-168. doi: 10.1016/j.tjem.2016.09.008. PMID: 27995208; PMCID: PMC5154590.