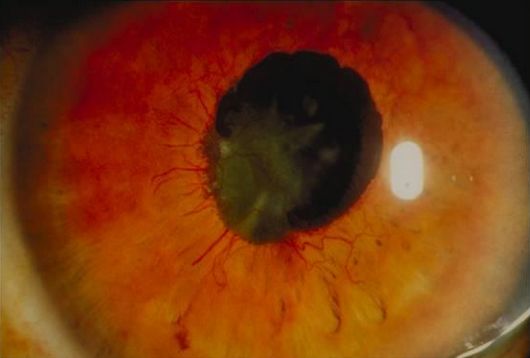
Definition: Neovascularization of iris
Pathophysiology: Causes that lead to retinal hypoxia triggers release of vasoproliferative factors include vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), fibroblast growth factor (FGF) and others
Etiology:
1. Diabetic Retinopathy
2. Retinal Vascular Occlusive Diseases
- Central Retinal Vein Occlusion (CRVO)
- Ischaemic Hemiretinal Vein Occlusion
3. Ocular Ischaemic Syndrome
- Carotid Artery Occlusive Disease
- Takayasu’s Syndrome
- Carotid-Cavernous Fistula
- Giant Cell Arteritis
- Wyburn-Mason syndrome
- Strabismus Surgery
- Ocular Radiation
4. Tumours
- Uveal Melanomas
- Metastatic Choroidal Tumours
- Medulloepithelioma
- Hypoxic Retinoblastoma
- Pigmented Ciliary Adenocarcinoma
- Metastatic Malignant Lymphoma
5. Others
- Uveitis
- Retinal Vasculitis
- Coat’s Disease (Retinal telangiectasia)
- Eales’ Disease (Periphlebitis retinae)
- Sarcoidosis
- X-linked Retinoschisis
- Chronic Retinal Detachment
- Retinopathy of Prematurity (ROP)
- Systemic Cryoglobulinaemia
Important causes:
- Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR)
- Central Retinal Vein Occlusion (CRVO)
- Sickle cell retinopathy
- Chronic iridocyclitis
- Retinoblastoma
Grading of rubeosis iridis:
- 0 : No iris neovascularization
- 1 : Less than 2 quadrants of NV at iris pupillary zone
- 2 : More than 2 quadrants of NV at iris pupillary zone
- 3 : Grade 2 + less than 3 quadrants of NV at iris ciliary zone and/or ectropion uveae
- 4 : More than 3 quadrants of NV at iris ciliary zone and/or ectropion uveae
Findings:
- Abnormal iris vessels
- Perform gonioscopy to assess presence of angle neovascularization
- May have elevated IOP (neovascular glaucoma)
Rubeosis Iridis and Neovascular glaucoma:
The disease develops in 3 stages:
1. Neovascularization of the iris (NVI)
2. Secondary open angle glaucoma (SOAG): The NVI extend to involve the angle, and are accompanied by fibrosis, blocking the trabecular meshwork and causing ocular hypertension, and SOAG.
3. Secondary angle closure glaucoma (SACG): Myofibroblasts within the fibrovascular tissue proliferate and contract, forming peripheral anterior synechiae (PAS), and secondary angle closure, with resulting intra-ocular pressure rise.
100 days glaucoma: Neovascular glaucoma (NVG) secondary to ischemic CRVO
Treatment:
- Ischemia: Panretinal Photocoagulation (PRP)
- IOP control: Glaucoma drainage implant (e.g. Molteno’s tube)
Good, it’s nice note, i really get new information about this topic