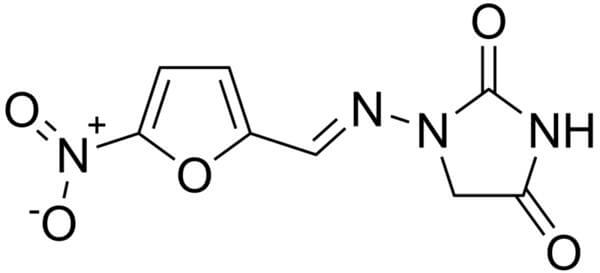
Recently, a wound swab culture and sensitivity reported an E.coli sensitive to Nitrofurantoin. But will it really be helpful in the wound infection?
Without a doubt, literatures claim that the sole use of the drug is in the treatment of Urinary Tract Infection (UTI), as after oral or intravenous (i.v.) administration, therapeutically active concentrations are attained only in urine. Nitrofurantoin can be adminsitered i.v. but this is rarely used and and the parenteral preparation is not generally available. Intravenous nitrofurantoin is unsuitable for the treatment of systemic infections of any kind because of poor serum levels.
Following absorption, concentrations of nitrofurantoin in blood and body tissues are low because of rapid elimination and therefore, antibacterial concentrations are not achieved. Nitrofurantoin should not be administered when the possibility of bacteremia exists, as the drug does not achieve therapeutic serum levels when administered orally.
The peak serum concentration after a single 100 mg oral nitrofurantoin dose is <2 µg/ml and the urine concentrations are known to be 50-200 µg/ml. MIC for most susceptible organisms is 32 µg/ml which is easily attained in urine but not in the serum and tissues.
Because of the low tissue levels, nitrofurantoin should not be used to treat UTI with associated renal cortical or perinephric abscess.
A high blood concentration of nitrofurantoin causes an axonal neuropathy.
Nitrofurazone is a topically used nitrofuran for wounds, burns and skin infections and for infections in skin grafts.
Conclusion:
- Nitrofurantoin must not be reported in sensitivity testing outside that of urine.
- Nitrofurantoin should only be used for uncomplicated UTI.
References:
Grayson M, Crowe S, McCarthy J, Mills J, Mouton J, Norrby S, et al. Kucers’ the use of antibiotics: A clinical review of antibacterial, antifungal and antiviral Drugs. 6th ed. Broca Raton: CRC Press; 2010.
Scholar EM. The antimirobial drugs. 2nd ed. Pratt WB, editor. USA: Oxford University Press; 2001 May 28.

He is the section editor of Orthopedics in Epomedicine. He searches for and share simpler ways to make complicated medical topics simple. He also loves writing poetry, listening and playing music. He is currently pursuing Fellowship in Hip, Pelvi-acetabulum and Arthroplasty at B&B Hospital.


i agree with this article because i went to the ER for a very painful UTI and a leg abcess. the dr cut my infection open and put a string to help it drain. i was perscribed Macrobid. my UTI is gone but my abcess is not. its a little bit better but not even close to being cured i think it might be spreading. after reading this ill be going to urgent care tonite. if i could find out this info w a simple online search i wonder how the dr did not know this was not effective.