Amidst the post-earthquake fear, we managed to complete our 15 days internship in the Dermatology department which was setup in the patient’s waiting hall. The posting went pretty well; the learning experience was fun – thanks to the teachers and seniors who provided us with friendly environment and guidance. A…
Category: Clinical Skills and Approaches
History taking and examination skills and Flowchart approaches to commonly encountered medical conditions and diseases.

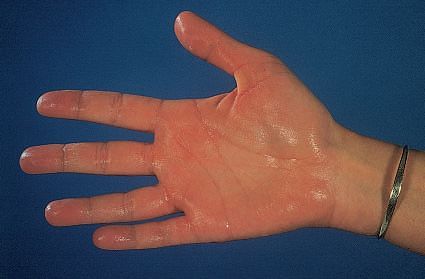
Examination of Hands
History: Hand dominance and occupation? Injury? Pain? Paresthesia? Impaired function? Swelling? Position: Place the patient’s hands on pillow Look: SEATS a. Shape or Deformity: – Wrist: Radial deviation: RA Ulnar deviation and flexion deformity: Spastic hemiplegia (CP) Wrist drop (also finger drop): Radial nerve injury Prominent dorsal ulnar and radial…
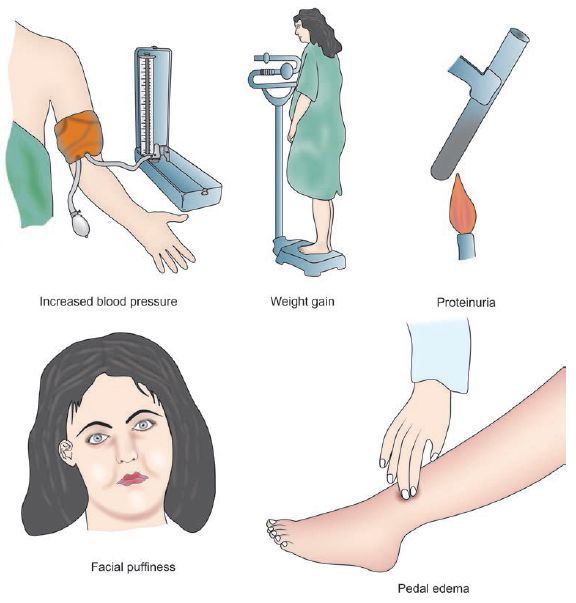
Approach to hypertension in pregnancy
Hypertension in pregnancy is one of the major cause of maternal, fetal and neonatal mortality and morbidity in both the developing and developed nations. About 10-15% of pregnancies are accompanied by hypertension and if these are detected early and effective interventions are performed, the prognosis is good. A. HISTORY FOR…
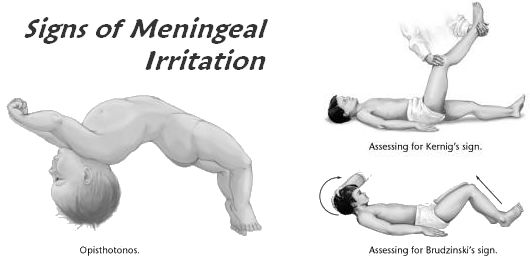
Meningeal signs
Meningitis refers to the inflammation of leptomeninges and underlying subarachnoid cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Meningism or meningismus is a morbid state characterized by a meningitic syndrome (a triad of headache, photophobia and nuchal rigidity) without intracranial inflammation. Some authors, have also used the term “meningism” or “meningismus” to describe the characteristic signs…
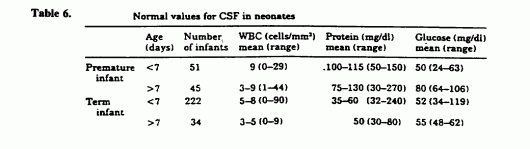
Practical Procedures : Lumbar Puncture (LP)
Synonyms: Spinal tap Definition: Puncture of subarachnoid space in the lumbar region of the spinal cord to withdraw cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) for diagnostic or therapeutic purpose or inject drugs for anesthetic purpose. Indications: A. Diagnostic: CNS infections: Bacterial, viral, fungal, parasitic or TB meningitis Subarachnoid hemorrhage Carcinomatosis meningitis (CNS involvement…

Pulsus Paradoxus – Clinical Examination
Synonyms: Paradoxical pulse, Paradoxic pulse, Reversed Bernheim sign Definition of Pulsus Paradoxus There is normal physiological fall in Blood pressure upto 10 mmHg during inspiration. Pulsus paradoxus is the exaggeration of this normal decline in blood pressure more than 10 mmHg during inspiration. The “paradox” refers to the fact that…
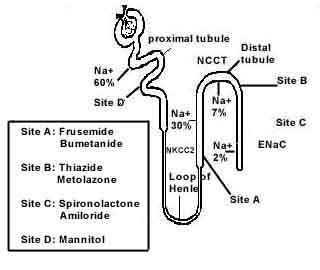
Approach to a Child with Edema
Before beginning the clinical approach to a child with edema, it is necessary to understand the basics of fluid compartments, starling forces and technique of eliciting edema. Life threatening causes of Edema: Generalized: Cardiac disease Congestive Heart Failure Pericardial effusion Renal disease Nephrosis Nephritis Hepatic failure Localized: Allergic reaction with…
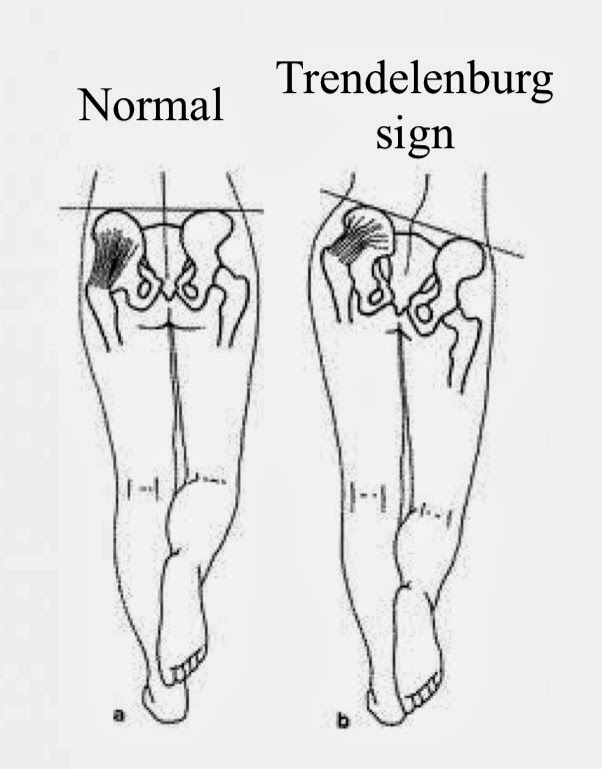
Trendelenburg test or sign
Method: The patient is then asked to stand on one leg and bend the opposite knee to 90° without flexing the hip. This action eliminates the role of hip flexors as they play a role in pelvic stability and may affect the Trendelenburg sign. The test is then repeated by…